Question 1 State the various functions of tongue?
Question 2 Name four different tastes which can be detected by our tongue?
Question 3 How many teeth does an adult man have? What is the number of different types of teeth?
Question 4 State the function of various types of teeth in mouth?
Question 5 Draw a sketch of the tongue?
Question 6 Which organ help in getting the taste of food we eat?
Question 7 Draw and explain the structure of teeth?
Question 8 What is meant by tooth decay? Name some of the foods which are the major causes of tooth decay?
Question 9 What are the various ways of preventing tooth decay?
Question 10 What is diarrhoea? How is diarrhoea caused?
Question 11 Why does dehydration take place in diarrhoea? How can dehydration be prevented?
Question 12 What is oral rehydration solution? When is it given to a person?
Question 13 What is the full form of ORS?
☛ Also Read NCERT Solutions for Chapter 2 Nutrition In Animals
Contents
Teeth
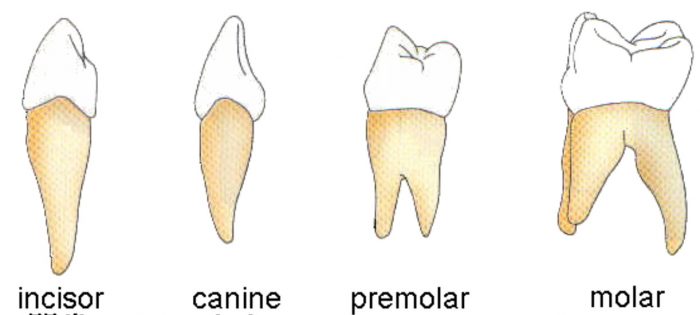
We chew the food with the teeth and break it down mechanically into small pieces. There are four types of teeth in our mouth. These are:
(1) Incisors,
(2) Canines,
(3) Premolars and
(4) Molars.
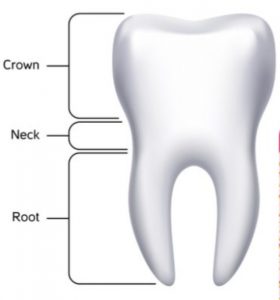
The upper part of a tooth (which we can see in the mouth) is called crown. The middle part of a tooth (which is inside the gums) is called neck whereas the lower part of a tooth (which is embedded in the jaw bone) is called root.
Every tooth is held in a separate socket in the jaw.
Different types of teeth differ in appearance and perform different functions.
1) Incisors
Incisors are the chisel shaped teeth at the front of the mouth. The incisors are for biting and cutting the food. There are four incisors in the centre of each jaw.
2) Canines
Canines are the large, pointed teeth just behind the incisors. The canines are for piercing and tearing the food. There are two canines in each jaw, one behind the left incisor and the other behind right incisor.
3) Premolars
Promolars are the large teeth just behind the canines on each side. Premolars have large, flat surfaces. The premolars are for chewing and grinding the food. There are four premolars in a jaw, two on each side.
4) Molars
Molars are very large teeth which are present just behind the premolars, towards the back of our mouth. Molars are for chewing and grinding the food. There are six molars in each jaw, three on each side. Molars are present only in the permanent set of teeth. They are not present in the temporary set of teeth called milk teeth.
Adult men and women have a total of 32 teeth. Of these, 16 are in the upper jaw and 16 are in the lower jaw. The 16 teeth of each jaw consist of 4 incisors, 2 canines, 4 premolars and 6 molars.
Milk Teeth and Permanent Teeth
In human beings, the teeth grow twice.
1) First time the teeth grow when one is a small baby (or infant) .This set of teeth is called milk teeth. They are a temporary set of teeth. The milk teeth loosen and begin to fall off at the age between 6 and 8 years.
2) When milk teeth fall off in a child, then another set of teeth grow in their place. So, second time the teeth grow when one is a child. The second set of teeth is called permanent teeth. The permanent teeth grow in place of milk teeth. The permanent set of teeth remains till the old age. But when old people lose their permanent teeth, then new teeth do not grow in their place.
Tooth Decay
The white, hard outer covering of tooth is called enamel. The part of tooth below the enamel is called dentine. Inside the dentine is pulp cavity which contains nerves and blood vessels.
Tooth decay is a process in which the tooth becomes rotten due to the formation of cavities (holes) inside it leading to toothache.
If we do not clean our teeth and mouth after eating food, then many harmful bacteria begin to grow and live on the teeth. These bacteria act on the sugar present in the left-over food particles sticking to the teeth to form acid. The acid thus formed eats up the enamel and dentine of the tooth gradually and ultimately makes a cavity (or hole) in the tooth. When this cavity (or hole) reaches the pulp cavity of the tooth (which contains nerves), our tooth becomes painful and we get tooth ace.
If the cavities caused by tooth decay are not treated in time (by fillings, etc.) by a dentist, then it causes severe toothache.
In extreme cases, tooth decay can lead to the loss of whole tooth (because it may require extraction).
Tooth decay can be prevented in the following ways:
1) We should rinse the mouth thoroughly with clean water after every meal.
2) We should clean our teeth with a brush and toothpaste at least twice a day.
3) A dental floss should be used to take out food particles trapped between the teeth.
4) We should eat less of sugary foods such as sweets, chocolates, toffees, and ice cream, etc.
5) Too many cold drinks should also be avoided.
Tongue
The tongue is a fleshy muscular organ in the mouth which is attached at the back to the floor of the buccal cavity (mouth cavity).
The various functions of the tongue are as follows:
1) The tongue helps in mixing saliva with food during chewing (which is essential for the digestion of food).
2) The tongue helps in swallowing the food into the food pipe.
3) The tongue helps in getting the taste of food.
4) The tongue is essential for talking (or speaking).
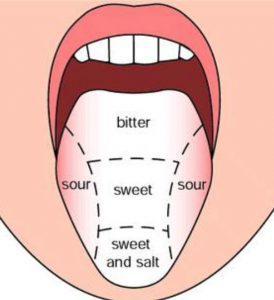
There are four types of tastes : sweet, salty, sour and bitter.
For example: sugar solution has a sweet taste, common salt solution has a salty taste, lemon juice has a sour taste whereas an extract of neem leaves or bitter gourd (karela) has a bitter taste.
The tongue has taste buds which detect different tastes of food. Our tongue has four kind
taste buds which detect sweet, salty, sour and bitter tastes. The taste buds for each of these tastes are located in different parts of the tongue.
Different parts of the tongue are sensitive to different tastes.
(1) Most taste buds at the front of the tongue detect sweet and salty tastes. The maximum effect of sweet taste is felt at the tip of the tongue whereas the maximum effect of salty taste is felt just behind the tip of the tongue.
(2) Most of the taste buds on the sides of the tongue detect sour taste.
(3) Most of the taste buds at the back of the tongue detect bitter taste.
Diarrhoea
The condition in which a person passes out watery stools frequently is called diarrhoea. Diarrhoea may be caused by an infection (due to disease causing micro-organisms), food poisoning or indigestion. Diarrhoea is very common in children.
Diarrhoea leads to the loss of water and salts from the body of a person (through frequent watery stools). The loss of water from the body of a person through watery stools is called dehydration.
The sudden loss of too much water (or dehydration) makes a person dangerously ill in a very short time. Excessive dehydration of body caused by diarrhoea can even lead to death
In order to prevent dehydration, the person suffering from diarrhoea should be given a solution of sugar and salt in clean water, many times a day. The solution of sugar and salt in water is called Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS) (because it is given to the person orally, through mouth). ORS makes up the loss of water and salt in the body. The sugar gives energy which helps in speedy recovery.
| Notes for Chapter 2 Nutrition In Animals |
What is the connection between teeth and tongue? I have this Question from so many days. And For that, I start My Research and During my Research I found this article, and this what I was Looking for In this Article I get My All the Answers and get some extra Knowledge. Thanks for sharing this useful stuff and Keep up the good work.
It is very helpful to me