Oxoacids of Phosphorus – The p-Block Elements – Class 12
Some Important Oxoacids of Phosphorus
Contents
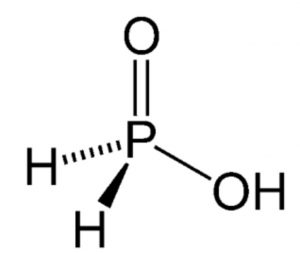
(1) Phosphinic acid or Hypophosphorous acid, H3PO2
Preparation of Phosphinic acid or Hypophosphorous acid
(1) It is prepared by heating phosphorus with alkalies like barium hydroxide when precipitate of barium phosphate is formed. The precipitate is separated and heated with a calculated amount of sulphuric acid.
3Ba(OH)2 + 2P4 + 6H2O —–> 2PH3 +3Ba(H2PO2)2
Ba(H2PO2)2 + H2SO4→ BaSO4 + 2H3PO2
Barium sulphate is separated by filtration and solution is concentrated when hypophosphorous acid separates out.
It has one P=0, one P-OH and two P-H bonds. Since it has only one P-OH bond, so it has only one ionizable hydrogen atom. Therefore, it behaves as monobasic acid, ionising as:
H3PO2 ⇔ H+ + H2PO2¯
The other two hydrogen atoms directly bonded to P are not ionizable. Due to the presence of two P–H bonds, the acid as well as it salt behave as strong reducing agents.
On heating to 313 K it decompose to phosphine
3H3PO2 ——> PH3 + 2H3PO3
However, on heating above 333K, it decomposes to phosphoric acid and phosphine
2 H3PO2 —–> H3PO4 + PH3
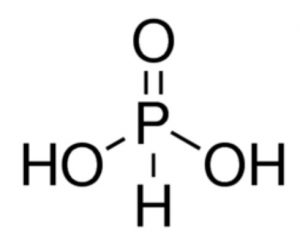
(2) Phosphorous acid or Phosphonic acid, H3PO3
Preparation of Phosphorous acid or Phosphonic acid
(1) It is prepared by the hydrolysis of phosphorus trichloride or trioxide.
PCl3 + 3H2O→ H3PO3 + 3HCl
P4O6 + 6 H2O –> 4 H3PO3
It has one P double bond O, one P-H and two P-OH bonds. Since it has two P-OH bonds, so it has two ionisable H atoms.
Therefore, it behaves as dibasic or diprotic.
H3PO3 ⇔ H+ + H2PO3¯ Ka1 = 1 x 10-2
H2PO3¯⇔ H+ + H2PO32- Ka2 = 2 x 10-7
On heating it decomposes into phosphoric acid and phosphine.
4 H3PO3 ———-> 3 H3PO4 + PH3
It is readily oxidised by air in the presence of a catalyst iodine into phosphoric acid.
2H3PO3 + O2 ———>2H3PO4
It is a strong reducing agent.
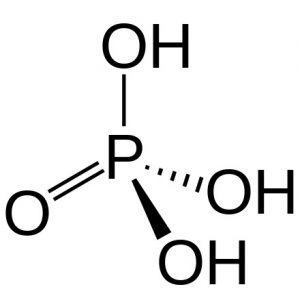
(3) Orthophosphoric acid, H3PO4
Preparation of Orthophosphoric acid
(1) It is prepared by adding phosphorus pentaoxide to water and boiling the solution.
P4O10 + 6H2O ——–> 4H3PO4
(2) It can also be prepared by heating phosphorus with cone. HNO3 or by dissolving PCl5 in water.
PCl5 + 4H2O ——-> H3PO4 + 5HCl
It has one P=0 and three P-OH bonds. Since it has three P-OH bonds, so it has three ionisable H atoms.
Therefore, it behaves as tribasic or triprotic and ionises in three stages :
H3PO4 ⇔ H+ + H2PO4¯ Ka1 = 7.5 x 10-3
H2PO4¯ ⇔ H+ + HPO42- Ka2 = 6.2 x 10-8
HPO42- ⇔ H+ + PO43¯ Ka3 = 1 x 10-13
Therefore, it forms three series of salts such as NaH2PO4 (disodium hydrogen phosphate), Na3HPO4 (disodium hydrogen phosphate) and Na3PO4 (sodium phosphate).
(4) Pyrophosphoric acid, H4P2O7
It contains phosphorus in +5 oxidation state.
Preparation of Pyrophosphoric acid
(1) It is prepared by heating orthophosphoric acid to 523K.
2H3PO4 —–> H4P2O7 + H2O
Structure of Pyrophosphoric acid
The acid is formed by the loss of a molecule of water from two molecules of phosphoric acid.
(a) Since it contains four OH groups, it is tetrabasic. It dissolves in water to form orthophosphoric acid.
2H4P2O7 + H2O —> 3 H3PO4
Orthophosphoric acid
(b) Upon strong heating, it decomposes to form meta phosphoric acid.
H4P2O7 —-> 2HPO3 + H2O
Metaphosphoric acid
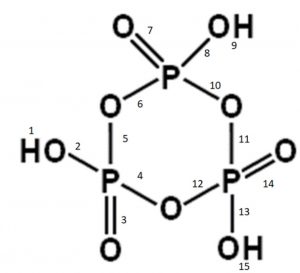
(5) Metaphosphoric acid, HPO3
It has one P-OH bond and therefore, exists as monobasic.
Preparation of Metaphosphoric acid
It is prepared by heating orthophosphoric acid to 525 K.
H3PO4 —-> HPO3+ H2O
Metaphosphoric acid does not exist as simple monomer, rather it exists as cyclometaphosphoric acid or polymetaphosphoric acid.
Leave a Reply