Contents
Potassium Permanganate, KMnO4
It is prepared from mineral pyrolusite (MnO2) by following steps :
1) Conversion of Pyrolusite ore to Potassium Manganate
The pyrolusite is fused with caustic soda or potassium carbonate in the presence of air or oxidising agent such as potassium nitrate or potassium chlorate to give a green mass due to the formation of potassium manganate.
2 MnO2 + 4KOH + O2 → 2K2MnO4 + 2 H2O
2 MnO2 + 2 K2CO3 + O2 → 2 K2MnO4 + 2CO2
MnO2 + 2 KOH + KNO3 → K2MnO4 + KNO2 + H2O
2) Oxidation of Potassium Manganate to Potassium Permanganate
The green mass is extracted with water resulting in green solution of potassium manganate. The solution is then , treated with a current of chlorine or ozone or carbon dioxide to oxidise potassium manganate to potassium permanganate. The solution is concentrated and dark purple crystals of potassium permanganate separate out.
2 K2MnO4 + Cl2 → 2 KCl + 2 KMNO4
2 K2MnO4 + O3 + H2O → 2 KMnO4 + 2 KOH + O2
3K2MnO4 + 2CO2 → 2K2CO3 + 2MnO2 + 2 KMnO4
Manganate ion also disproportionate in a neutral or acidic solution to give permanganate
3 MnO42- + 4 H+ → 2 MnO4¯ + MnO2 + 2H2O
The alkaline potassium manganate solution is electrolytically oxidised.
Electrolytic Method
Potassium permanganate is prepared by alkaline oxidative fusion of MnO2 followed by electrolytic oxidation of manganate (VI).
The potassium manganate solution is taken in an electrolytic cell which contains iron cathode and nickel anode.
The Potassium manganate solution is taken in anodic compartment while dilute solution is added in the cathode compartment.
When the current is passed the manganate ion is oxidised to permanganate ion at anode and hydrogen is liberated at cathode.
2 K2MnO4 ⇔ 2 K+ + MNO4 2-
At anode
MNO4 2- → MnO4¯ + e-
(green) (purple)
At cathode
2 H+ + 2 e → 2H
2H → H2
Laboratory preparation
It is prepared by oxidising a manganese (II) ion salt by peroxodisulphide.
2Mn2+ + S2O82- + 8H2O → 2MNO4– + 10 SO42- + 16H+
Properties of Potassium Permanganate
1) Colour and melting point : It is a dark violet crystalline solid having a metallic lusture. It has m.p.523 K.
2) Solubility : It is fairly soluble in water giving a purple solution.
3) Action of heat : When heated strongly to 513 K , it decomposes to give oxygen.
2 KMnO4 → K2MNO4 + MnO2 + O2
At red heat potassium manganate formed decomposes into potassium manganite and oxygen.
2 K2MnO4 → 2 K2MNO3 + O2
4) Action of alkalies
On heating with alkalies, potassium permanganate changes into potassium manganate and oxygen gas is evolved.
4KMnO4 + 4KOH → 4K2MnO4 +2 H2O + O2
5) Oxidising character
It is a powerful oxidising agent in neutral , alkaline or acidic solution because it liberates nascent oxygen
In Neutral solution MnO2 is formed
2 KMnO4 + H2O → 2 KOH + 2 MNO4 + 3O
MnO4¯ + 2 H2O + 3 e¯ → MnO2 + 4 OH‾
In strongly alkaline solution manganate ions are formed
2 KMnO4 + H2O → 2 K2MnO4 + H2O + O
MnO4¯ + e‾ → MnO42-
Eq. wt. of KMnO4 = Mol wt. / 1 = 158 /1 =158
Potassium manganate is further reduced to MNO2 in the presence of a reducing agent.
K2MnO4 + H2O → MnO2 + 2 KOH + O ] × 2
MnO42- + 2 H2O + 2 e¯ → MnO2 + 4 OH¯
2 KMnO4 + H2O → 2 MNO2 + 2 KOH + 3O
2 MNO4¯ + 2 H2O + 3 e‾ → MnO2 + 4OH¯
In Acidic solution
Mn2+ ions are formed
2 KMnO4 + 3 H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2 MnSO4 + 3 H2O + 5 O
MnO4¯ + 8H+ + 5e¯ → Mn2+ + 4 H2O
The oxidation reactions of acidified KMnO4 are :
1) It oxidises acidified ferrous salts (green) to ferric salts (yellow)
2 KMnO4 + 3 H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2 MnSO4 + 3 H2O + 5 O
2 FeSO4 + H2SO4 +O → Fe2(SO4)3 + H2O ] × 5
______________________________
2 KMnO4 + 10 FeSO4 + 8 H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2 MnSO4 + 5 Fe2(SO4)3 + 8 H2O
______________________________
or 2 MnO4¯+ 10 Fe2+ + 16 H+ → 2 Mn2+ + 10 Fe3+ + 8 H2O
2) It oxidises hydrogen sulphide to sulphur
2 KMnO4 + 3 H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2 MnSO4 + 3 H2O + 5 O
H2S + O → H2S + S ] × 5
______________________________
2 KMnO4 + 5 H2S + 3 H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2 MnSO4 + 5 S + 8 H2O
______________________________
or 2 MnO4¯+ 5S2- + 16 H+ → 2 Mn2+ + 5S+ 8 H2O
3) It oxidises acidified potassium iodide to iodine
2 KMnO4 + 3 H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2 MnSO4 + 3 H2O + 5 O
2 KI + H2SO4 + O → K2SO4 + H2O + I2 ] × 5
______________________________
10KI + 2 KMnO4 + 8 H2SO4 → 6 K2SO4 + 2 MnSO4 + 8 H2O + 5 I2
______________________________
or 10 I¯ + 2 MnO4¯ + 16 H+ → 2 Mn2+ + 8 H2O + 5 I2
4) It oxidises sulphur dioxide to sulphuric acid
2 KMnO4 + 3 H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2 MnSO4 + 3 H2O + 5 O
SO2 + H2O + O → H2SO4 ] × 5
______________________________
2 KMnO4 + 5SO2 + 2 H2O → K2SO4 + 2 MnSO4 + 2 H2SO4
______________________________
or 2MnO4 ¯ + 5 SO2 + 2 H2O → 5 SO42– + 2 Mn2+ + 4 H+
5) It oxidises nitrites to nitrates
2 KMnO4 + 3 H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2 MnSO4 + 3 H2O + 5 O
KNO2 + O → KNO3 ] × 5
______________________________
2 KMnO4 + 5 KNO2 + 3 H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2 MnSO4 + 5 KNO3 + 3 H2O
______________________________
or 2MnO4¯ + 5 NO2 + 6 H+ → 2 Mn2+ + 5 NO3‾ + 3 H2O
6) It oxidises oxalates or oxalic acid to carbon dioxide
2 KMnO4 + 3 H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2 MnSO4 + 3 H2O + 5 O
C2H2O4 + O → 2 CO2 + H2O ] × 5
______________________________
2 KMnO4 + 5 C2H2O4 + 3 H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2 MnSO4 + 10 CO2 + 8 H2O
______________________________
or 2MnO4¯ + 5 C2O4 2– + 16 H+ → 2 Mn2+ + 8 H2O + 10 CO2
7) It oxidises hydrogen halides to halogen
2 KMnO4 + 3 H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2 MnSO4 + 3 H2O + 5 O
2 HX + O → H2O + X2 ] × 5
______________________________
2 KMnO4 + 10 HX + 3 H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2 MnSO4 + 8 H2O + 5 X2
______________________________
or 2MnO4¯ + 10 X¯ + 6 H+ → 2 Mn2+ + 8 H2O + 5 X2
8) It oxidises sulphites or sulphurous acid to sulphates or sulphuric acid
2 KMnO4 + 3 H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2 MnSO4 + 3 H2O + 5 O
Na2SO3 + O → Na2SO4 ] × 5
______________________________
2 KMnO4 + 3 H2SO4 + 5 Na2SO3 → K2SO4 + 2 MnSO4 + 5 Na2SO4 + 3 H2O
______________________________
or 2 MnO4¯ + 5 SO32- + 6 H+ → 2 Mn2+ + 5 SO42- + 3 H2O
In Neutral Medium
1) It oxidises hydrogen sulphide to sulphur
2 KMnO4 + H2O → 2 KOH + 2 MnO2 + 3 O
H2S + O → H2S + S ] × 3
______________________________
2 KMnO4 + 3 H2S → 2 KOH + 2 MnO2 + 2 H2O + 3 S
or 2 MnO4¯ +3 H2S → 2 MnO2 + 3S + 2 H2O + OH¯
2) It oxidises manganese sulphate to manganese dioxide
2 KMnO4 + H2O → 2 KOH + 2 MnO2 + 3 O
MnSO4 + H2O + O → MnO2 + H2SO4 ] × 3
2KOH + H2SO4 → K2SO4 + 2 H2O
______________________________
2 KMnO4 +3 MnSO4 + 2 H2O → 5 MnO2 + K2SO4 + 2 H2SO4
______________________________
or 2 MnO4– + 3 Mn2+ + 2 H2O → 5 MnO2 + 4 H+
3) It oxidises sodium thiosulphate to sodium sulphate or sulphur.
8 KMnO4 + 3 Na2S2O3 + H2O → 8 MnO2 + 3 Na2SO4 + 2 KOH + 3 K2SO4
or 8 MnO4¯ + 3 S2O32- + H2O → 8 MnO2 + 6 SO42- + 2 OH¯
In Alkaline Medium
1) It oxidises iodides to iodates in alkaline solution
2 KMnO4 + H2O → 8 MnO2 + 2 KOH + 3 O
KI + 3O → KIO3
______________________________
2 KMnO4 + KI + H2O → 2 MNO2 + 2 KOH + KIO3
______________________________
2 MnO4¯ + I¯ + H2O → 2 MnO2 + IO3¯ + 2 OH¯
2) Alkaline KMnO4 oxidises ethylene to ethylene glycol
C2H4 + H2O + O → C2H4(OH)2
Uses of Potassium Permanganate
1) It is used as an oxidising agent in the laboratory in volumetric analysis for the estimation of ferrous salts , oxalates , iodides and hydrogen peroxide.
2) It is used as a disinfectant and germicide. It is used to purify well water.
3) It is used in industry as a strong oxidising agent.
4) Alkaline potassium permanganate is used in organic chemistry under the name Baeyer’s reagent.
5) It is used for the bleaching of wool, cotton , silk and other textile fibres.
6) It is used for decolorisation of oils because of its strong oxidising agent.
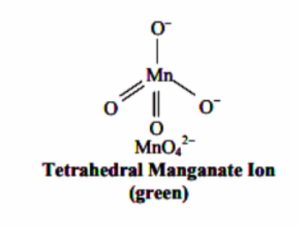
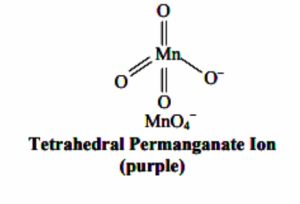
Structure of MnO4¯and MnO42- ion
Permanganate and manganate ion have tetrahedral shape. The four atoms are arranged tetrahedrally around manganese. The pi bonding takes place by the overlap of p-orbital of oxygen with d-orbital of manganese.
Important Note
1) Potassium permanganate is not a primary standard because it is not available in the pure state and contain traces of MnO2. It is therefore standardised with a standard solution of oxalic acid or sodium oxalate.
2) Potassium permanganate titrations are carried out only in the presence of dil H2SO4 because oxygen produced from the reaction of KMnO4 with dil H2SO4 is used only for oxidising the reducing agent.
3) HCl or HNO3 can not be used in place of H2SO4 .
a) If HCl is used , the oxygen produced by the reaction of KMnO4 and dil HCl will be partially used to oxidise HCl to chlorine.
b) If HNO3 is used , it itself acts as an oxidising agent and will partially oxidize the reducing agent.
Leave a Reply