Contents
Methods of preparation of Coordination Compounds
(1) Substitution reactions
The majority of complexes are prepared by substitution reactions. The general method of synthesis is to replace water molecules surrounding the metal ion by other ligands. For example:
(a) When an aqueous solution of CuSO4 is heated with excess of ammonia, it gives deep blue coloured [Cu(NH3)4]2+ species.
Some other examples are:
(2) Redox Reactions
An aqueous solution of oxalic acid and potassium oxalate reduces K2Cr2O7 to the complex ion trioxalatochromate (III) ion.
(3) Direct Combination of Reactants
Metal amines can be prepared by the direct addition of a metal salt to liquid ammonia.
NiCl2 + 6NH3 → [Ni(NH3)6]Cl2
Importance of Coordination Compounds
(1) Estimation of Hardness of Water : Hardness of water is estimated by simple titration with Na2 EDTA. The Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions form stable complexes with EDTA. The selective estimation of these ions can be done due to differences in the stability constants of calcium and magnesium complexes.
(2) In qualitative and Quantitative Analysis : The complex formation method is used in qualitative scheme of analysis. The familiar colour reactions given by metal ions with a number of ligands (especially chelating ligands) as a result of formation of coordination entities form the basis for their detection and estimation by classical and instrumental methods of analysis.
Some common reagents used are EDTA, DMG (dimethyl glyoxime), cupron, α-nitroso-β-naphthol, etc.
For example
(i) It is used in group I for the separation of silver ion from the precipitate of AgCl, Hg2Cl2 and PbCl2. We add aqueous ammonia solution to the precipitate when silver chloride dissolves due to the formation of the complex [(Ag(NH3)2]+ ion.
Hg2Cl2 and PbCl2 do not form complexes and therefore, do not dissolve.
(ii) Cd2+ ions can be tested in the presence of Cu2+ ion by forming their complexes with KCN. Copper forms [Cu(CN)4]3- which ionizes less than [Cd(CN)4]2-. On passing H2S only Cd2+ ions will be precipitated as CdS while Cu2+ ions will not be precipitated. This application is also called masking of ions.
(iii) Fe3+ ions are tested by adding potassium ferrocyanide solution to the salt solution when ferri ferrocyanide or Prussian blue complex is formed.
Potassium ferricyanide
(iv) Ni2+ ions are detected by adding dimethylglyoxime (DMG) in the presence of NH4OH to nickel salt solution when a brilliant red precipitate is formed due to the formation of a complex of Ni2+ with DMG.
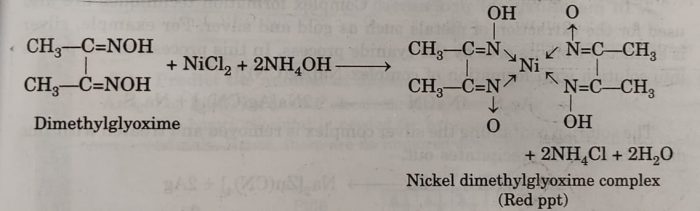
This method is also used for the estimation of Ni2+ ions.
(v) The presence of Co2+ ions is tested by adding ammonium thiocyanate solution when a blue colour is obtained due to the formation of a complex:
Co(CNS)2 + 2NH4CNS → (NH4)2[Co(CNS)4]
Co2+ ions can also tested by adding potassium ferricyanide solution when a reddish brown precipitate is formed due to the formation of an insoluble complex :
(vi) The presence of Zn2+ ions is tested by adding potassium ferrocyanide solution to the acidified salt solution when a bluish white precipitate is formed due to the formation of a complex :
(3) In electroplating : The coordination compounds of silver and gold are used as constituents of electroplating baths for controlled delivery of metal ions for reduction.
(4) In water treatment : Complex compounds like sodium metapolyphosphate are used to remove Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions from hard water by forming complexes with these ions. This prevents the scale formation in boilers.
(5) In dyeing : Mordants are insoluble substances which are uniformly deposited in the fibres to be dyed. These mordants can then attach to the molecules of the dyes by complex formation and help in fixing the dye to the fibres in a stable form. The important mordants used are Fe(OH)3 and Al(OH)3.
(6) Biological importance : Many biological important natural compounds exist as coordinated complexes.
For Example:
(7) In metallurgical processes : Complex formation techniques are also used for the extraction of metals such as gold and silver.
For Example
(i) silver is extracted from its ores by the cyanide process. In this process, silver passes into solution with formation of complex Na[Ag(CN)2].
(ii) The cyanide process is used for the extraction of gold. It is based on the fact that gold dissolves in aqueous potassium cyanide solution in the presence of atmospheric oxygen to form a soluble cyanide complex :
The solution containing gold complex is filtered and treated with zinc dust to get gold.
Similarly, purification of metals can also be achieved through formation and subsequent decomposition of their coordination compounds.
(8) In catalysis : Certain coordination compounds act as catalysts for different reactions.
For example: pentacarbonylcobalt (II) acts as a catalyst in the hydrogenation of alkenes. During hydrogenation, Co(II) is oxidised to Co(III).
The coordination compounds are used as homogeneous catalysts for a variety reactions in solution.
These are also used as heterogeneous catalysts in many reactions.
(9) In photography : In black and white photography, the developed film is fixed by washing with hypo solution which dissolves the undecomposed AgBr to form a complex ion, [Ag(S2O3]3-
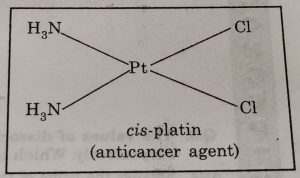
(10) In medicines : Complexing agents are used for removal of metal poisoning. A platinum complex, [PtCl2(NH3)2] known as cis-platin has been used in cancer therapy.
EDTA is used in the treatment of lead poisoning.
Very good approach to spreading free education to everyone.