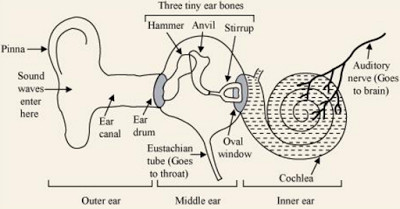
Part of the ear which we see outside
1)Pinna:Board part
2)Ear canal:2-3 cm long passage
3)Ear drum(Tympanum):At the end of ear canal is thin,elastic and circular membrane.
Middle Part
1)It consist of three small and delicate bones called hammer,anvil and stirrup .They are linked to each other.
2)Eustachian Tube:The lower part of middle ear has a narrow tube going to the throat.It connects middle ear to throat and ensures that air pressure inside middle ear is same as that on the outside.
Inner Part
1)Cochlea:Coiled tube
One side is connected to middle ear through elastic membrane over window.The cochlea is filled with a liquid.The liquid contains nerve cells which are sensitive to sound.the other side of cochlea is connected to auditory nerve which goes into the brain.
Working
Sound waves—->Pinna—–>ear canal—–>Fall on ear drum
Sound waves consist of compression(high pressure regions)and rarefaction(low pressure region).
When compression of sound waves strikes ear drum the pressure on the outside of membrane increases and forces the eardrum to move inward.
When rarefaction of sound waves strikes ear drum the pressure on the outside of membrane decreases and forces the eardrum to move outward.
When sound waves fall on ear drum,it starts vibrating back and forth rapidly.Vibrating ear drum causes hammer to vibrate.
Hammer—–>Anvil—–>Stirrup(Vibration passes)—–>Oval window—-> Liquid of cochlea.
The vibrating liquid of cochlea sets up electrical impulse in nerve cell present in it.These impulses are carried by auditory nerve to the brain.The brain interprets these electrical impulses as sound and we get sensation of hearing.
Good and simple answer for kids. Keep it up.
Explained very simply and in a way that students can easily understand and remember
It’s very easy to draw and label
Very clearly explained ,keeping in view that recipient is student of ninth class.
It helper me very much.Thank You,
Nice explanations
Thanks for explanation..
It’s really helpfull……..Thank you.