Question 1 What are the ways in which physical state of matter can be changed ?
Question 2 What is boiling ?
Question 3 What is condensation?
Question 4 What is freezing?
Question 5 What do you mean by inter-conversion of matter?
Question 6 What is melting or fusion.
Question 7 What does higher melting point indicate ?
Question 8 How does a solid changes into liquid on heating ?
Question 9 How does a liquid changes into vapours on heating ?
Contents
Can Matter change its State?
We can change the physical state of matter in two ways:
(1) By changing Temperature (heating or cooling)
(2) By changing Pressure (increasing or decreasing)
Effect of change of Temperature
(a) Increasing Temperature
solid → liquid → gas
(b)Decreasing temperature
Gas → Liquid → Solid

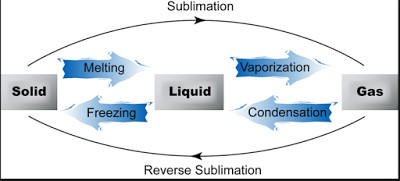
(1) Solid to Liquid (Melting)
Ice → Water
The process in which a solid substance changes into a liquid on heating is called Melting or fusion. The temperature at which a solid substance melts and changes into a liquid at atmospheric pressure is called melting point of the substance. For Ex: The ice melts at a temperature of 0°C to form liquid water. So the melting point of ice is 0°C.
Different solids have different melting points.
For Example: Melting point of iron is 1535°C .Melting point of wax is 63°C
Higher the melting point of solid substance, greater will be the forces of attraction between its particles.
When a solid substance is heated, the heat energy makes its particles vibrate more vigorously. At the melting point, the particles of a solid have sufficient kinetic energy to overcome the strong forces of attraction holding them in fixed positions and break to form small groups of particles. And the solid melts to form a liquid.
(2) Liquid to Gas (Boiling or Vaporisation)
Water → Steam
The process in which a liquid substance into a gas rapidly on heating is called boiling.
When water changes into steam rapidly on heating, it is called boiling of water.
The temperature at which a liquid boils and changes rapidly into a gas at atmospheric pressure is called boiling point of the liquid.
For Example: When water is heated to a temperature of 100°C ,it boils rapidly to form a gas called steam, so the boiling point of water is 100°C.
Different liquids have different boiling points.
For Example: The boiling point of alcohol is 78°C
The boiling point of mercury is 357°C.
The boiling point of a liquid is a measure of the forces of attraction between its particles. Higher the boiling of a liquid, greater will be the forces of attraction between its particles.
When a liquid is heated, the heat energy makes its particle move even faster. At the boiling point the particles of a liquid have sufficient kinetic energy to overcome the forces of attraction holding them together and separate into individual particles.
(3) Gas to Liquid (Condensation)
Steam → Water
The process of changing a gas or vapours to liquid by cooling is called condensation.
(4) Liquid to Solid (Freezing)
Water → Ice
The process of changing a liquid into a solid by cooling is called freezing.
Freezing is the reverse of melting.
Very nice work madmji
I enjoy
AFTER LONG STRUGGLE…….YOU DO BEST WORK FOR NATION
Nice mam