Question 1 What is meant by the phases of the Moon? What causes the phases of the moon?
Question 2 What is the difference between full moon and a new moon?
Question 3 What is a satellite? Name the natural satellite of the Earth?
Question 4 Moon does not have light of its own? How are we able to see the moon?
Question 5 State two differences between artificial and natural satellite?
Question 6 What is an artificial satellite? Name artificial satellite launched ?
Question 7 State few uses of artificial satellite?
Question 8 Write the full form of INSAT and IRS?
Question 9 What is meant by remote sensing?
Satellites
A satellite is a celestial body that revolves around a planet. Earth is a planet and Moon revolves around the Earth, therefore, Moon is a satellite of the Earth.
Mercury and Venus, do not have satellites. All the remaining six planets have one or more satellites.
The satellites revolve around the planets due to the gravitational pull of the planets. The satellites have no light of their own. The satellites shine and become visible to us because they reflect the light of the Sun falling on them.
Moon
(1) Moon is a natural satellite of the Earth.
(2) The moon revolves around the Earth on a definite regular path-the Moon orbit’s.
(3) The gravitational attraction of the Earth holds the Moon in its orbit.
(4) The Moon is about one-fourth the size of the Earth in diameter but its mass is only about one-eightieth that of the Earth.
(5) Moon is the closest celestial object to the Earth.
(6) Moon appears to be much bigger than the stars because it is much more nearer to the Earth than the stars.
(7) Moon’s surface is covered with hard and loose dirt. There are many craters of different sizes on the surface of Moon.
(8) The surface of Moon has also a large number of steep and high mountains.
(9) Since there is no air or water on the Moon, therefore, there is no life on the Moon.
(10) On the Moon, days are extremely hot and nights are extremely cold.
(11) The first man to land on Moon was an American astronaut Neil Armstrong in July 1969. He was followed by another astronaut Edwin Aldrin shortly afterwards.
We are able to see the Moon because the sunlight falling on the Moon gets reflected towards the Earth. When the sunlight falls on Moon, then a part of this sunlight is reflected by the surface of Moon towards the Earth. When this reflected sunlight enters our eyes on the Earth, to us it appears as if the light is coming from the Moon itself . Since the sunlight reflected by Moon enters our eyes, we are able to see the Moon. Thus, Moon shines with the sunlight reflected by it. The Moon reflects sunlight towards us even during daytime but we cannot see the Moon during daytime due to the glare of the Sun. We can see the Moon only during night time when the Sun is not present in our sky.
Phases of Moon
The Moon always shows the same face (or same side) to the Earth as it rotates on its axis. This is because the Moon completes one rotation on its axis in the same time which it takes to complete one revolution around the Earth. So, we never see the back side of the Moon from the Earth.
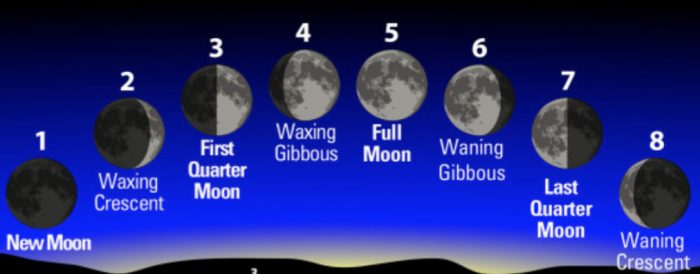
(1) The day (or rather night) on which the Moon is not visible at all is called the new Moon day. We have a very dark night on this day of the month.
(2) On the next day, only a small, curve like portion of the Moon appears in the night sky. This is known as the Crescent Moon.
(3) Thereafter, every night, the size of the bright, visible part of the Moon appears to become bigger and bigger, giving us many shapes including half Moon or first quarter moon and more than half Moon or waxing gibbous.
(4) After fifteen days (from the new Moon day), we can see the whole bright disc of the Moon in the night sky. So, there is also one day in a month when the Moon is visible as a perfectly round ball of light in the sky. The night on which the whole bright disc of Moon is visible to us on the Earth is called the full Moon day. We have the maximum moonlight during the night on this day of the month.
(5) Thereafter, every night, the size of the bright, visible part of the Moon goes on becoming smaller and smaller.
(6) And after fifteen days (from the full Moon day), the Moon is not visible again. We have the new Moon again. This new Moon will again change into full Moon after another fifteen days, and the process is repeated endlessly.
The shape (or appearance) of the visible part of the Moon changes everyday over the whole month. And this change is repeated again and again, month after month. The different shapes (or appearances) of the bright, visible part of the Moon as seen from the Earth (during a whole month) are called phases of the Moon.
Moon shines and becomes visible to us because it reflects sunlight falling on it towards the Earth. But since the Moon revolves around the Earth and the Earth revolves around the Sun, we cannot see all of the sun-lit surface of Moon from the Earth all the time. We can see only that part of the sun-lit surface of Moon which is towards us. Depending upon the relative positions of the Sun, the Moon and the Earth, we see different amounts of the Sun lit surface of Moon from the Earth.
The phases of Moon occur due to its continuously changing position with respect to the Earth and the Sun.
(1) When the Moon is on the side of Earth nearest to the Sun, then the side of Moon which is lit by Sun is away from Earth. And the side of Moon which is towards the Earth is in darkness. In this position, Moon appears to be in darkness from Earth and hence cannot be seen. This is called new Moon.
(2) As the Moon moves in its orbit around the Earth from position 1 to 2, we can see a small sun-lit portion of its surface. This is called crescent Moon.
(3) As the Moon moves further from position 2 to positions 3 and 4, the sun-lit portion of Moon facing the Earth becomes bigger and bigger giving us half Moon and more than half Moon. This is called the waxing phase (increasing phase) of the Moon.
(4) After fifteen days from new Moon day, the Moon reaches in position 5 which is on the side of Earth farthest from the Sun . In this position , the whole sun-lit side of the Moon is towards the Earth, and we see the Moon as a full round disc of bright light. This is called full Moon.
(5) As the Moon moves around the Earth further from position 5 to positions 6, 7 and 8, the sun-lit portion of Moon facing the Earth becomes smaller and smaller. This is called the waning phase (decreasing phase) of the Moon. And ultimately Moon completes the revolution around the Earth and again reaches position 1. So, we have new Moon once again.
We can have one new Moon and one full Moon during a month (which is the time taken by Moon to complete one revolution around the Earth).
The time period between one full Moon and the next full Moon is actually 29½ days.
In the moon-based calendars (catted lunar calendars) this period of 29½ days is taken as a month.
Artificial Satellite
A man-made space-craft placed in orbit around the Earth is called an artificial satellite. An artificial satellite is placed in orbit around the Earth with the help of a launch vehicle called rocket.
Rocket carries the artificial satellite from the Earth to a height of a few hundred kilometres above it and gives it a sideways push.
The motion of artificial satellite around the Earth is maintained by the gravitational pull of the Earth. In this way, the artificial satellite keeps on revolving around the Earth continuously, without stopping.
The main differences between the artificial satellites of the Earth and its natural satellite Moon are as follows:
(1) The artificial satellites are much nearer to the Earth than its natural satellite Moon.
(2) The height (or distance) of the artificial satellites from the Earth (and hence their speed around the Earth) can be adjusted according to our needs. This is, however, not possible with the natural satellite of Earth called Moon.
The artificial satellites carry a large variety of equipment and instruments inside them.The electricity required for running the equipment in an artificial satellite is provided by solar cells.
The technique of collecting information about an object from a distance (without making a physical contact with the object) is called remote sensing. Remote sensing satellites can scan the Earth’s surface very closely with their cameras and infra-red sensors, even while orbiting high above the Earth.
The important applications (or uses) of artificial satellites are:
(1) Artificial satellites are used for communications such as long distance transmission of television programmes, radio programmes, telephone calls and internet. The artificial satellites used for communications purposes are called Communications Satellites.
(2) Artificial satellites are used for weather forecasting (such as rain-fall, snow-fall, etc.) and for giving advance warning of floods and cyclones, etc. Weather forecasting is done by using artificial satellites called Weather Satellites (or Meteorological Satellites) which are a kind of remote sensing satellites
(3) Artificial satellites are used for surveying the natural resources of the Earth like minerals, agricultural crops and potential fishing zones in the sea, etc. This is done by using the artificial satellites called remote sensing satellites.
(4) Artificial satellites are used for spying for military purposes (like observing the movement of enemy troops and military equipment, taking pictures of enemy air-fields and harbours, etc). Remote sensing satellites are used for spying for military purposes.
(5) Artificial satellites are used to collect information about other planets, stars and galaxies, etc. The artificial satellites used for studying celestial objects are called Astronomy Satellites.
The first artificial satellite launched by India was Aryabhatta. It was launched in 1975. Some other Indian satellites are Bhaskara, INSAT, IRS, Rohini, Kalpana-1 and EDUSAT.
INSAT stands for Indian National SATellite
IRS stands for Indian Remote-sensing Satellite
EDUSAT stands, for EDUcation SATellite
The Agency responsible for the development of space science programmes in our country is Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)

Leave a Reply