Question 1 State few characteristics of image formed by a plane mirror?
Question 2 What is a periscope?
Question 3 State the various uses of periscope?
Question 4 Explain how a hair dresser makes you see hair at the back of your head after the hair cut is complete?
Question 5 How many images of an object will be formed when the object is placed two plane mirrors which are inclined at the following angles:
a) 120° b)45° c) 180° d) 60° e) 90°
Question 6 When an object is placed between two plane mirror inclined at an angle, then multiple images are formed? Explain?
Question 7 How can you show that white light consist of seven colours?
Question 8 What is meant by dispersion of light?
Question 9 How plane mirrors in Kaleidoscope arranged?
Question 10 Explain the construction and working of periscope?
Question 11 What happens when a beam of light is passed through a glass prism?
Question 12 What is the use of Kaleidoscope?
Contents
Characteristics of Image Formed by a Plane Mirror
(1) The image formed by a plane mirror is virtual (or unreal).
(2) The image formed by a plane mirror is behind the mirror.
(3) The image formed in a plane mirror is the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it.
(4) The image formed in a plane mirror is of the same size as the object.
(5) The image formed by a plane mirror is erect
(6) The image in a plane mirror is laterally inverted.
Explanation
(1) Image formed by a plane mirror is virtual, we mean that the image formed by a plane mirror cannot be obtained on a screen. It can be seen only by looking into the plane mirror.
For example : When we look into a plane mirror, we see the image of our face. Our image in the plane mirror is virtual (or unreal). Our image seen in the plane mirror cannot be formed on a screen placed behind the plane mirror.
(2) The image in a plane mirror is the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it. We mean that if a person is standing at a distance of 1 metre in front of a plane mirror, then his image will be formed at the same distance of 1 m behind the plane mirror.
(3) The dimensions of image are exactly the same as that of the object. The image is neither enlarged (neither bigger than the object) nor diminished (nor smaller than the object).
For example : If a person is 1.75 metre tall, then his image in the plane mirror will also be exactly 1.75 metre tall.
(4) The image of an object in a plane mirror is erect, we mean that the image in plane mirror is the same side up as the object, the top of object is the top of image and bottom of object is the bottom image.
For example : If we look into a big plane mirror, we will see the image of our whole body. We will notice that our image in the plane mirror has head on the top and feet at the bottom just like us.
(5) The image in a plane mirror is laterally inverted, we mean that the image in a plane mirror is sideways reversed with respect to the object. In an image formed by a plane mirror, the left side of object appears on the right side in the image whereas the right side of object appears on the left side in the image. Change of sides of an object and its mirror image is called lateral inversion.
For example : If we stand in front of a plane mirror and lift our left hand, then our image in the plane mirror appears to lift its right hand. And if we lift our right hand, then our image in the plane mirror appears to lift its left hand. This means that the left side of our body becomes the right side in the mirror image whereas the right side of our body becomes left side in the mirror image. Our image in the plane mirror is laterally inverted (or sideways reversed).
Reflected Light can be reflected again
If the rays of light reflected by a plane mirror are incident on another plane mirror, then the reflected rays are reflected again. The reflected rays of the first plane mirror become incident rays for the second plane mirror.
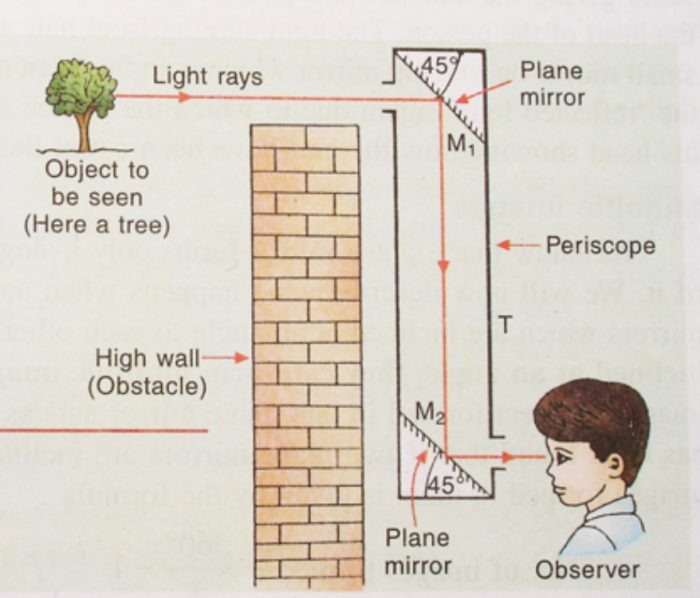
Periscope
An optical instrument (or device) in which reflected light is periscope.
A periscope is a long, tubular device through which a person can see objects that are out of the direct line of sight.
By using a periscope, we can see the objects on the other side of a high wall which cannot be seen by us directly. The periscope makes use of two plane mirrors to see over the top of things.
Principle of Periscope
A periscope works on the reflection of light from two plane mirrors arranged parallel to one another.
Arrangement of Periscope
(1) A periscope consists of a long tube T having two plane mirrors M1, and M2 fitted at its two ends.
(2) The two plane mirrors are fitted in such a way that they are parallel to one another and their reflecting surfaces face each other.
(3) Each plane mirror, however, makes an angle of 45° with the side of the tube.
(4) There are two holes in the periscope tube: one hole is in front of the top mirror M1 and other hole is in front of the bottom mirror M2.
Working of Periscope
(1) The upper hole of periscope is turned towards the object to be seen so that the top mirror M1 , faces the object.
(2) We look into the periscope from the bottom hole in front of lower mirror M2. The light rays coming from the object fall on the plane mirror M1.
(3) Mirror M1 reflects these rays of light downwards, towards the second mirror M2. The mirror M2 then reflects the reflected rays of light towards the eye of the person looking into the periscope through the lower hole.
(4) Since the light rays coming from the object enter the eye of the person (or observer), it is possible to see the image of object through the periscope.
Some of the Uses of Periscopes
(1) A periscope is used to see over the heads of a crowd.
(2) A periscope is used by soldiers sitting in a trench (or bunker) to observe the enemy activities outside(over the ground).
(3) A periscope is used by a navy officer sitting in a submarine to see ships over the surface of water in the sea (even though the submarine itself may be submerged under water)
Reflected light can be reflected again enables a person to see the hair cut at the back of his head at a hair dresser’s shop. After giving the hair cut to a person, the hair dresser holds a small plane mirror behind the head of the person. The light coming from hair at the back of head is reflected by this small mirror on to a big mirror which is in the front of the person. This big mirror reflects the ‘reflected light again due to which the person can see the image of the back hair of his head showing how the hair have been cut at the back side of his head.
Multiple images
When two plane mirrors are kept inclined at an angle, they can form multiple images of an object. This is because the image of object formed in one plane mirror acts as object for the other plane mirror.
If two plane mirrors are inclined at an angle x, then the number of images formed in them is given by the formula:
No. of images formed = ( 360° /x ) – 1
Thus, two plane mirrors inclined at an angle of 90° form three images of an object placed between them.
If we take two plane mirrors, set them at right angles to each other (with their edges touching), and place a coin in-between these mirrors, then we will see three images of the coin in the two plane mirrors.
| Angle between two plane mirror | No. of images formed |
| 180° | 1 |
| 120° | 2 |
| 90° | 3 |
| 60° | 5 |
| 45° | 7 |
| 0° | infinite |
As the angle between the two plane mirrors decreases, the number of images formed increases.When the two plane mirrors become parallel to each other, then an infinite number of images are formed.
We can see a large number of images of ourselves if we stand before two plane mirror hanging on opposite walls. This is because our image formed in one mirror acts as object for the other mirror, and this process goes on and on, resulting in a large number of images. We can not see all the images because they become fainter and fainter with the increasing number of reflections of light.
Kaleidoscope
The kaleidoscope is an instrument or toy containing inclined plane mirrors which produce multiple reflections of coloured glass pieces (or coloured plastic pieces) and create beautiful patterns.
Construction of kaleidoscope
(1) The kaleidoscope consists of three long and narrow strips of plane mirrors inclined at 60° to one another forming a hollow prism, and fitted into a cardboard tube.
(2) One end of the cardboard tube is closed by an opaque disc (cardboard disc) having a small hole at its centre.
(3) The other end of cardboard tube is closed with two circular discs of glass : the inner disc being of transparent glass (clear glass) and the outer disc of ground glass (translucent glass).
(4) A number of small pieces of different coloured glass (or plastic) and having different shapes are kept between the two glass discs (which can move around freely in the space between the two glass discs).
5) When we hold the kaleidoscope tube towards light and look inside it through the small hole, we see beautiful patterns of coloured glass. Actually, the coloured glass pieces act as objects and the inclined plane mirrors form multiple images of these glass pieces by repeated reflections, which look like beautiful patterns or designs.
6) If we turn the kaleidoscope tube slightly, the glass pieces will rearrange and produce a new pattern.
7) A kaleidoscope produces hundreds of ever-changing coloured patterns (or designs). In Kaleidoscope we can never see the same pattern again. Every time a new pattern is formed. Kaleidoscopes are used by designers of wall papers and fabrics, as well as by artists to get ideas for new patterns.
Sunlight – White or coloured
The sunlight is referred to as white light. The white sunlight actually consists of seven colours.
Activity
Take a glass prism and place it on a table in a darkened room. Place a white cardboard screen at some distance behind the prism. Allow a thin beam of sunlight (coming through a tiny hole in the window) to fall on the prism. We will see that the beam of white sunlight splits on entering the glass prism and forms a broad patch of seven colours (called spectrum) on the white screen placed on the other side of prism.
The splitting up of white light into seven colours on passing through a transparent medium like a glass prism is called dispersion of light.
The formation of spectrum (band of seven colours) shows that white sunlight is made up of seven colours. The seven colours of the spectrum of white light are: Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange and Red.
Rainbow in the sky is a natural phenomenon showing the dispersion of sunlight. Rainbow is produced by the dispersion of sunlight by tiny rain drops suspended in the atmosphere (which act as tiny prisms made of water). The formation of rainbow also tells us that sunlight consists of seven colours.

Leave a Reply