Question 1 Name few sources of water?
Question 2 Which is the largest source of water on the earth?
Question 3 How is sea water different from river water?
Question 4 Name one natural source of saline water?
Question 5 Name three states of matter?
Question 6 How does water help in the dispersal of seeds of plants and trees?
Question 7 How water is used to generate electricity?
Question 8 Name few fresh water sources?
Also Read NCERT Solutions for Chapter 14 Water
Water
Water is essential for life. All the living things (plants and animals) need water to live. We need water for drinking, cooking food, washing utensils, cleaning floor, brushing teeth, bathing, washing clothes, flushing toilets and watering plants.
Uses of water
Some of the important uses of water in different fields are as follows:
(1) Water is used in homes for drinking, cooking food, washing utensils, cleaning floor, brushing teeth, bathing, washing clothes, flushing toilets and watering plants. These are the domestic uses of water. Water is also used by animals for drinking purposes.
(2) Water is used in agriculture for growing food. Water is needed to grow all kinds of crop plants which provide us food. The largest amount of water is used for irrigation of crops in agriculture. Water of ponds, lakes and rivers is used for growing fish (which is used as food by many people)
(3) Water is used in industries for producing almost all the things that we use. The making of paper, cloth, medicines, chemicals, bread, biscuits, and many, many other things in industries requires a lot of water.
(4) Water is used to keep things cool. For example: water is used in the radiators of vehicles (like cars, buses and trucks) to keep their engines cool.
(5) Water in the rivers and the seas is used for transporting passengers and goods from one place to another by boats, sailing boats, motor boats and ships.
(6) Water of rivers and the sea helps in the dispersal of seeds of several plants and trees. The seeds of various plants and trees located near the banks of rivers and sea-shores fall on the water of rivers and the sea. These seeds float on water and are carried away to far away places. When these seeds reach the land, they germinate to produce plants and trees in that area.
(7) Water is used to generate electricity: At a hydroelectric power plant, water stored in a high dam is allowed to fall gradually from a great height. This fast moving water turns the turbines (water-wheels). The rotating turbines then run the generators which produce electricity. At thermal power plants, water is boiled to make steam (by burning coal, oil or gas). The high pressure steam turns the steam turbines. The rotating steam turbines run the generators which produce electricity.
Sources of Water
The water which we use is obtained from sources such as : Rivers, Lakes, Ponds, Wells and Springs. The water which we get in taps in our homes comes from rivers, lakes or tube-wells. The water of rivers, lakes and ponds contains some suspended impurities, soluble impurities and germs (like bacteria). So, the river water, lake water and pond water is not fit for drinking as such. It has to be purified first.
1. The rivers get their water from the melting of snow lying on the peaks of snow mountains (called glaciers) and also from rains.
2. Lakes, ponds and wells get their water from rains.
Thus, the two major sources of water on land are glaciers (snow mountains) and rains. Though the water formed by the melting of snow of glaciers is very pure in the beginning but it gets contaminated with impurities when it flows in rivers. Rain water is the purest form of natural water. Rain water is not salty. It is fit for drinking. Rain water also becomes contaminated and impure when it flows into rivers, lakes and ponds. Some of the rain water which falls on earth seeps through the soil and goes down under the surface of earth. This water is stopped by some hard rocks and collects there.
This underground water is called well-water. The water of a deep well is usually fit for drinking. The place where underground water comes out on the surface of earth on its own is called a spring. Spring water is also fit for drinking. The rivers, lakes, ponds, wells, springs, rain and glaciers are called fresh water sources. Their water does not contain much dissolved salts. More than two-thirds of the earth is covered with water.
Most of this water is in oceans and the seas. So, the largest source of water on the earth are oceans.Being highly saline (or salty) ocean water or sea water is not fit for drinking, other domestic purposes, agriculture or industrial needs. It is very expensive to purify sea water and make it fit or drinking purposes. Oceans and seas are not fresh water sources.
Oceans, however, play an important role in supplying the fresh water which we use. It is from the salty water of oceans that we get non-salty fresh water by a natural process called water cycle. It is the water cycle in nature which converts highly salty ocean water (or sea water) into pure water which then freezes to form snow on high mountains, falls on earth as rain, flows into rivers, fills lakes and ponds, and also seeps into ground to provide us well water.
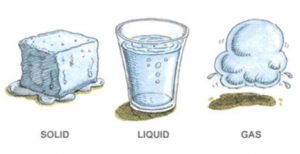
States of Water
(1) The ice which we take out from the freezer of a refrigerator is ‘frozen water (or ‘solidified water). So ice is solid water. Ice is the water in solid state. The water which falls from the sky as white flakes of ice during winter in extremely cold regions is called snow. Snow is also solid state of water.
(2) The water which flows from the tap is a liquid. Thus, tap water is the liquid state of water.
(3) Water vapour is the ‘gas state (or ‘gaseous state) of water. Water vapour is present in air. Since water vapour is a colourless gas, we cannot see water vapour in air. Very hot water vapour is called steam. Steam is also gaseous state of water. We can make steam ourselves.
If we heat some water in a beaker continuously by keeping the beaker over a burner, then after some-time the water starts boiling to form steam.
Ice, water and water vapour are the same substance but they are in different physical states: ice is a solid, water is a liquid whereas water vapour is a gas. Thus water can exist in three states : solid, liquid and gas. Water can be changed from one state to another by heating or cooling. For example
(1) When ice (or snow) is heated, it melts and changes into water.
(2) When water is cooled too much, it freezes and changes into ice (or snow).
(3) When water is heated, it evaporates and changes into water vapour.
(4) When water vapour is cooled, it condenses and changes into liquid water.
The water cycle in nature involves many physical processes such as evaporation, transpiration, condensation, freezing and melting. The heat energy required to run water cycle in nature is provided by the sun.
| Notes for Chapter 14 Water |
This was nice.
Thanks for helping me