Question 1 What is meant by refining of metals?
Question 2 Define the term electrolytic refining?
Question 3 How will you refine copper by electrolytic refining?
Refining
The process of purifying impure metal is called refining of metal.
The most important and most widely used method for refining impure metals is called electrolytic refining.
Many metals like copper, zinc, tin, lead, nickel, silver, gold are refined electrolytically.
For the refining of an impure metal by electrolysis:
1) A thick block of impure metal is made anode(It is connected to the positive terminal of the battery)
2) A thin strip of the pure metal is made cathode(It is connected to the negative terminal of the battery)
3) A water soluble salt(of the metal to be refined)is taken as electrolyte.
On passing electric current, impure metal dissolves from the anode and goes into the electrolytic solution. And pure metal from the electrolyte deposits on the cathode. The soluble impurities present in the impure metal go into the solution whereas the insoluble impurities settle down at the bottom of the anode as anode mud.
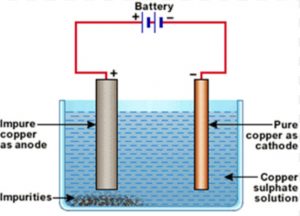
Electrolytic Refining of Copper
1) The electrolytic tank containing acidified copper sulphate solution as electrolyte.
2) A thick block of impure copper metal is made anode.
3) A thin strip of pure copper metal is made cathode.
On passing electric current, impure copper from the anode dissolves and goes into copper sulphate solution and pure copper from copper sulphate deposits on cathode. Thus pure copper metal is produced on the cathode. The soluble impurities go into the solution whereas insoluble impurities collect below the anode as anode mud.
At cathode
Cu2+ + 2 e– —> Cu
At anode
Cu – 2 e– —–> Cu2+
Thanking you for this post on Air from class 10
Thanks for the update