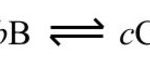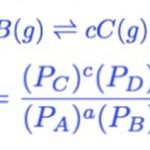Application of Equilibrium constant 1) Predicting the extent of reaction The magnitude of the equilibrium constant gives an idea of the relative amount of the reactants and the products. a) larger value of the equilibrium constant ( > 103 ) shows that forward reaction is favoured i.e. concentration of products is much larger than that of the reactants … [Read more...] about Application of Equilibrium Constant
Class 11
Types of Chemical Equilibria
Types Of Chemical Equilibria 1) Homogeneous Equilibria When in an equilibrium reaction, all the reactants and the products are present in the same phase , it is called homogeneous equilibrium. Type 1 : In which the number of moles of products is equal to the number of moles of reactants H2 + I2 2HI N2 + O2 2NO CO + H2O CO2 + H2 Type 2 : In which the … [Read more...] about Types of Chemical Equilibria
Expression and Units Of Equilibrium Constant
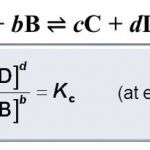
Expression for Equilibrium constant ( K ) The active mass of a pure solid is constant irrespective of its amount and if a pure liquid is present in excess, its active mass is also constant.In both the cases we put active mass equal to 1. Molar concentration of a substance means mol L-1 of the substance which is obtained by dividing the amount of the substance in moles by … [Read more...] about Expression and Units Of Equilibrium Constant
Relationship between Kp and Kc
where Δn = ( c + d ) - ( a + b ) Δn = No. of moles of gaseous products - No. of moles of gaseous reactants … [Read more...] about Relationship between Kp and Kc
Law of Chemical Equilibrium
At equilibrium, The rate of forward reaction = Rate of backward reactionThe above mathematical equation is called the Law Of Chemical Equilibrium. The product of the molar concentration of the products, each raised to the power equal to its stoichiometric coefficients divided by the product of the molar concentration of the reactants, each raised to the power equal to … [Read more...] about Law of Chemical Equilibrium