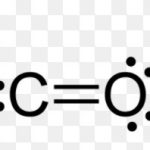Preparation 1) It is formed by incomplete combustion of carbon and carbon containing fuels. 2 C + O2 ------> 2 CO This type of incomplete combustion occurs during burning of petrol or diesel in automobile and therefore CO is always present in automobile exhausts. It is also present in volcanic gases and gases coming out of furnaces. 2) In the laboratory , pure … [Read more...] about Carbon Monoxide
p-Block Elements
Chemical Properties of Carbon Family
Oxidation State (1) Oxidation state of Carbon The general valence shell electronic configuration of elements of group 14 is ns2 np2 where n is the number of outermost principal shell. These elements can attain inert gas configuration either by losing or gaining 4 electrons forming M4+ or M4- ions. The C4+ ion does not exist firstly because it is a highly charged species … [Read more...] about Chemical Properties of Carbon Family
Physical Properties Of Carbon Family
Group 14 include Carbon (C), Silicon (Si), Germanium(Ge), tin(Sn), lead(Pb) and ununquadium (uuq) which is radioactive. Occurrence Carbon is the 17th most abundant element by weight in the earth crust. It occurs in the native state in form of coal ,graphite and diamond. In combined state it occurs widely as metal carbonates, hydrocarbons ,carbohydrates and carbon … [Read more...] about Physical Properties Of Carbon Family
Chemical Properties of Boron Family
Oxidation State The elements of group 13 have to two electrons in the s- orbital and one electron in the p-orbital of the valence shell. These elements are expected to show a uniform oxidation state of +3. Boron and aluminium which show an oxidation state of +3 only but gallium, indium and thallium due to inert pair effect show oxidation state of both +1 and +3 . As we … [Read more...] about Chemical Properties of Boron Family
Anomalous Behaviour Of Carbon
Carbon, the first member of group 14 ,shows an anomalous behaviour i.e. differ from rest of the members of its family. The main reason for this difference are : 1) exceptionally small atomic size b) higher electronegativity c)higher ionisation enthalpy d) absence of d orbital in the valence shell The main point of differences are: 1) Carbon in form of … [Read more...] about Anomalous Behaviour Of Carbon