NCERT Solutions for Geography, Chapter 5 – Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
Intext Questions
Page 43
Question 1. Why are the southern slopes in Himalayan region covered with thick vegetation cover as compared to northern slopes of the same hills?
Answer The growth of vegetation depends upon the amount sunlight and rainfall received. The southern slopes of the Himalaya receive more rain due to the south west monsoon winds which travel west along the southern slops. The northern slopes do not receive any such rainfall. So the southern slopes are covered with thick vegetation as compared to the northern slopes.
Question 2. Why have the western slopes of the Western Ghats covered with thick forests and not the eastern slopes?
Answer It is because the western slope get much heavier rainfall than the eastern slopes. Moisture laden air moves eastwards across, the Western Ghats during the monsoon season.
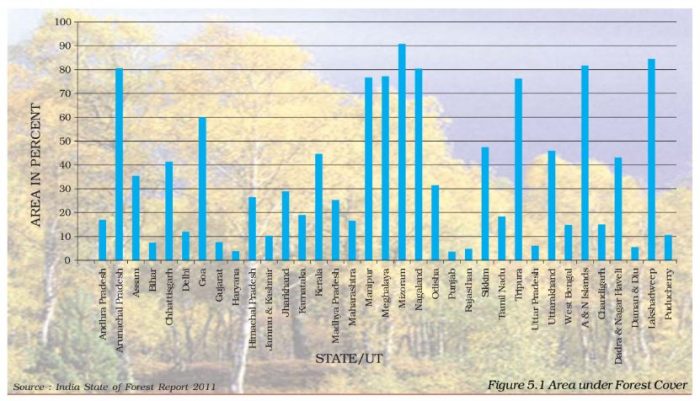
Question 3. Study the bar graph and answer the following questions
(i) Name the state having maximum area under forest cover.
(ii) Name the union territory having minimum area under forest cover and give the reason why.
Answer
(i) Nagaland
(ii) Lakshadweep is the union territory having minimum forest cover. Since Lakshadweep consists only of coral islands, they have no proper soil for growing of forests except for coconut trees. Since these are commercially viable there is no declared forest in Lakshadweep.
Page 47
Question 1. What will happen if plants and animals disappear from the Earth’s surface? Can human beings survive under such a situation? Why is biodiversity necessary and why should it be conserved?
Answer
(a) If the plants and animals disappear from the Earth’s surface, then the ecological balance will be disturbed. Without plants there will be no oxygen available for breathing after some time and everybody will die.
(b) Biodiversity means biological diversity, 1.e., there are many animal and plant species on our planet spread all over the world. These animal and plant species, including humans, are all interdependent
(c) Each species has its own place and role to play in the environment and help in the maintaining the ecological balance. That’s why it should be conserved.
Page 48
Question 1. Identify some medicinal plants in your area. Which plants are used as medicines by local people to cure diseases?
Answer Some medicinal plants found in our area with diseases they can cure are given below :
(i) Bel Fruit : The ripe fruit cures gastro intestinal problems.
(ii) Iswarmula Root : Its decoction cures constipation.
(iii) Satawari Tuber : It cures gastro intestinal problems.
(iv) Iswarmula Root : Decoction of root is given in constipation and abdominal colic.
(v) Dimiri Leaf and Stem : Fresh juice (50-100 mL) of leaves is given with water for about 10 days to treat gastro intestinal problems.
Page 50
(i) Find out from the above newspaper cuttings the main concern highlighted in the given news items.
Answer The main concern highlighted in the given news items is that wildlife in India is endangered and some species may get extinct soon. The rhinos, tigers, vultures and gulls are being killed by poachers or are dying.
(iii) Find out various steps taken by the Indian Government to protect them.
Answer The Indian Government has taken the following steps to protect the endangered species of flora and fauna
(a) Fourteen biosphere reserves have been established in the country in which the species are protected. It is illegal to kill any animals in them.
(b) Project Tiger, Project Rhino and Project Great Indian Bustard have been started to help protect these endangered species.
(c) Many National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries have been set up in various parts of the country.
(d) Many awareness programmes like release of advertisements, conduct of seminars, etc are undertaken by the Government to sensitise the general public to these issues.
(iv) Describe how you can contribute to the protection of endangered animals and birds.
Answer We can contribute to protect the endangered animals and birds in the following ways
(a) If we find any illegal activity like poaching, trapping, etc being carried out in our area, we should report it to the Forest Department office in the area.
(b) We can conduct awareness programmes about wildlife preservation in our locality and community for all people.
Exercises
Page 51
Question 1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below
(i) To which one of the following types of vegetation does rubber belong to?
(a) Tundra
(b) Tidal
(c) Himalayan
(d) Tropical Evergreen
Answer (d)
(ii) Cinchona trees are found in the areas of rainfall more than
(a) 100 cm
(b) 50 cm
(c) 70 cm
(d) less than 50 cm
Answer (a)
(iii) In which of the following states is the Simlipal Bioreserve located?
(a) Punjab
(b) Orissa
(c) Delhi
(d) West Bengal
Answer (b)
(iv) Which one of the following bioreserves of India is not included in the world network of bioreserve?
(a) Manas
(b) Nilgiri
(c) Gulf of Mannar
(d) Nanda Devi
Answer (a)
Question 2. Answer the following questions briefly
(i) Define an ecosystem.
Answer All the plants and animals in an area are interdependent and interrelated to each other in their physical environment, thus forming an ecosystem. Human beings are also an integral part of the ecosystem. They utilise the vegetation and wild life.
(ii) What factors are responsible for the distribution of plants and animals in India?
Answer The factors responsible for the distribution of plants (flora) and animals (fauna) in India are
(a) Relief factors
- Land
- Soil
(b) Climate
- Temperature
- Precipitation
- Photoperiod (sunlight)
(iii) What is a bioreserve? Give two examples.
Answer A bioreserve is an area in which the flora and fauna of the given country is protected and there are certain researches which are done on them. It is an area containing a wildlife preserve bordered by a buffer zone in which more frequent use is permitted to the public, established as a way of integrating habitat conservation with the interests of the local community.
Examples are Rajaji in Uttarakhand and Simlipal in Orissa.
(iv) Name two animals having habitat in tropical and montane type of vegetation.
Answer Animals found in Tropical forests are lion, tiger, pig, deer and elephant.
Animals found in Montane forests are Kashmir stag, spotted deer, wild sheep, jack rabbit, Tibetan antelope, yak, snow leopard, squarrels, shaggy horn wild ibex, bear and rare red panda, sheep and goats with thick hair.
Question 3. Distinguish between
(i) Flora and Fauna
(ii) Tropical Evergreen and Deciduous Forests
Answer
Difference between Flora and Fauna
| Flora | Fauna |
| The term flora is used to denote plants of a particular region or period. | The species of animals are referred to as fauna. |
| They make their food by photosynthesis. | They cannot make their own food and herbivore animals are dependent on flora for food. |
Difference between Tropical Evergreen and Deciduous Forests
| Tropical Evergreen Forests | Tropical Deciduous Forests |
| They grow in areas of heavy rainfall 200 cm and above. | They grow in areas receiving rainfall between 200 cm and 70 cm. |
| There is no definite time for trees to shed their leaves. | The trees shed their leaves for about 6 to 8 weeks in the dry summer. |
| Ebony, mahogany , rosewood, rubber and cinchona are the important trees of these forests. | Teak, Bamboo, Sal, Shisham, Sandalwood, Khair Kusum, Arjun, Peepal and Neem are the important trees of these forests. |
| Common animals found in these forests are elephants, monkeys, lemur, deer and the one horned rhinoceros. | Common animals found in these forests are lion tiger, deer and elephant. |
| Plenty of birds, bats sloth, Scorpions and shails are also found in these jungles. | A huge variety of birds, lizards, snakes and tortoises are found in these forests. |
| These forests are found in areas of the Western Ghats and the island group of Lakshadweep, Andaman and Nicobar, upper parts of Assam and the Tamil Nadu coast. | These forests are found mostly in eastern part of India, north eastern states along the foothills, the Himalayas, Jharkhand, Orissa, Chhattisgarh, on the western slopes of Western Ghats, Madhya Pradesh Bihar and Uttar Pradesh. |
Question 4. Name the different types of vegetation found in India and describe the vegetation of high altitudes?
Answer The following major types of vegetation are found in India
(a) Tropical Evergreen Forests
(b) Tropical Deciduous Forests
(c) Tropical Thorn Forests and Scrub
(d) Montane Forests
(e) Mangrove Forests
Vegetation of High Altitude (Montane Forests)
(a) In mountainous areas, the decrease in temperature with increasing altitude leads to a corresponding change in natural vegetation.
(b) The wet temperate type of forests are found between a height of 1000 and 2000 metres, where evergreen broad leaf trees such as oaks and chestnuts predominate.
(c) Temperate forests containing coniferous trees like pine, deodar, silver fir, spruce and cedar are found between 1500 and 3000 metres.
(d) These forests cover mostly the southern slopes of the Himalayas, places having high altitudes in southern and north east India.
(e) Temperate grasslands are common at higher elevations.
(f) At high altitudes, generally more than 3,600 metres above sea level, alpine vegetation is found. Silver fir, jumpers, pines and birches are the common trees of these forests.
Question 5. Quite a few species of plants and animals are endangered in India? Why?
Answer (a) Many plants and animals in India are endangered because of the greediness of human beings for their commercial value. Humans are hunting animals for their skins, horns and hooves which are in demand and give a lot of profit.
(b) Deforestation on a wide scale destroys the habitat of animals and also leads to decline of the different species of trees and plants. Ecological balance is disturbed due to deforestation, which is harmful for both flora and fauna.
Question 6. Why has India a rich heritage of flora and fauna?
Answer India has rich heritage of flora and fauna because of the following factors
(a) It has a very large geographical area which includes the mountains, the Northern plains, plateaus and also islands.
(b) lndia has a varied climate from very dry to monsoon type and temperature ranges from very hot to cold and very cold, which is suitable for different kinds of flora and fauna.
(c) India has different types of soil like alluvial soil, red soil and black soil suitable for different plant types.
(d) India is blessed with perenial rivers which sustain aquatic life apart from supporting different kinds of flora and fauna.
(e) The mountains and plains are capable of supporting and sustaining different kinds of plants and trees and provide an environment and habitat for various kinds of animal species.
India is one of the twelve mega biodiversity countries of the world. It has about 47,000 plant species. It stands at the tenth place in the world and fourth in Asia in plant diversity. It has 89,000 species of animals as well as a rich variety of fish. It has about 15,000 flowering plants and ferns. India is blessed with different types of soils, climatic conditions and physical features and thus, it is suitable for supporting different species of flora and fauna making it a biodiversity hot spot.
Map skills
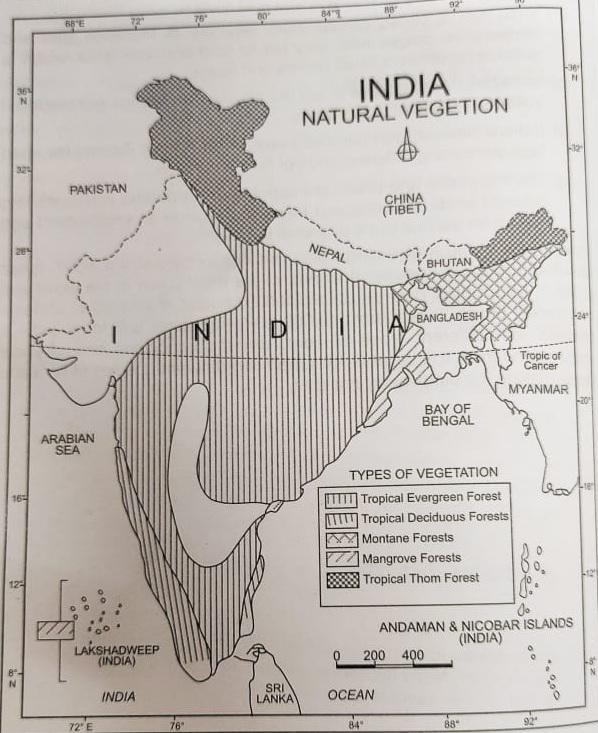
Answer (i) and (ii)
The Evergreen forests are labelled as ‘Tropical Evergreen Forest
The Dry Deciduous Forests are those parts of the forests labelled Tropical Deciduous Forests which have rainfall between 70 and 100 cm annually. They are found in the rainier part of the Peninsular plateau and the plains of Bihar and Uttar Pradesh.
(ii) Some National Parks in the four regions of India are listed below.
| Region | Name of National Parks |
| Northern | Dachigam and Rajaji |
| Southern | Bandipur and Guindy |
| Eastern | Kaziranga and Manas |
| Western | Gir and Sanjay Gandhi |
Project/Activity
(i) Find some trees in your neighbourhood having medicinal values.
(ii) Find ten occupations getting raw material from forests and wild life.
(iii) Write a poem or paragraph showing the importance of wild life.
(iv) Write the script of a street play giving the importance of tree plantation and try to enact it in your locality.
(v) Plant a tree either on your birthday or one of your family member’s birthday. Note the growth of the tree and notice in which season it grows faster.
Answer
(i) Some trees having medicinal values are (there are many others)
(a) Amla Plant or Indian Gooseberry: This is one of the richest sources of Vitamin C. It is a medium size deciduous plant, which attains a height of 8 to 18 meters. Amla is used to make herbal products, which helps get rid of health-related problems like hair fall, haemorrhage, leucorrhoea, skin diseases and discharge of blood from uterus.
(b) Neem Tree: It plays a significant role in Ayurvedic medicine. It helps to treat chickenpox, fever, skin disease and headache.
(c) Eucalyptus : It is a tall tree, with heights upto 100 metres. Oil taken out of the Eucalyptus leaves has great medicinal value. It helps in purifying blood and lowering of blood sugar level. It cures problems of asthma, bronchitis, cardiac problems and fungal infections.
(ii) Occupations getting following raw materials from forests and wildlife
(a) Carpentry
(b) Rubber industry
(c) Leather industry
(d) Ayurvedic medicine manufacturing
(e) Paper industry
(f) Glue industry
(g) Fruit and food production industry
(h) Hunting
(i) Resin extractor
(i) Perfume industry
(iii) Importance of Wildlife : Wildlife comprises of the innumerable varieties of wild plants, animals, fungi and microorganisms that exist on our planet Earth, rather than just cultivated plants and domesticated animals. We largely depend on this wildlife for every elementary requirement in our life.
The food we eat, the clothes, we wear, the medicines we consume, a variety of building materials used for construction, numerous chemicals used for manufacturing our necessities, all are extracted from the wildlife existing around us. About 40,000 species of plants, animals, fungi and microscopic animals benefit us in some way or the other. The normal functioning of the biosphere depends on endless interactions amongst animals, plants, and microorganisms.
This, in turn, maintains and improves human life further. These ecological processes are vital for agriculture, forestry, fisheries and other processes that support human life. Besides, there are severe biological processes wherein wildlife plays a key role, such as pollination, germination, seed dispersal, soil generation, nutrient cycling, habitat maintenance, waste breakdown, and pest control.
Leave a Reply