NCERT Solutions for Economics,
Chapter 2 – Economics People As Resource
Intext Questions
Page 17
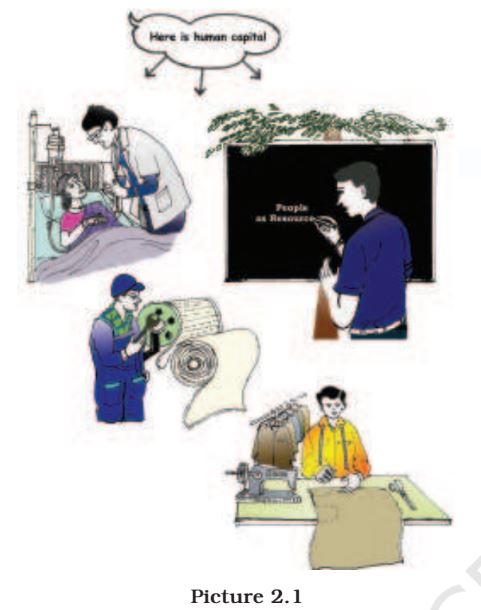
Question 1. Looking at the photograph can you explain how a doctor, teacher, engineer and a tailor are an asset to the economy?
Answer
(i) A population becomes human capital when there is investment made in the form of education training and medical care.
(ii) Human capital is the stock of skills and productive knowledge embodied in them.
(iii) Investment made in the form of education and training in making a doctor, a teacher an engineer an a tailor, has increased their capabilities of providing different services to the people of the country and therefore they are an asset to the economy of a nation.
Page 18
Question 1. Do you notice any difference between the two friends? What are those?
Answer The differences between the two friends Sakal and Vilas were
(i) Vilas’s father died when Vilas was two years old whereas Sakal was living with his parents.
(ii) Sakal went to school but Vilas did not go to school.
(iii) Sakal was interested in studies whereas Vilas was not interested in studies.
(iv) Sakal did a course in computers and became employed whereas Vilas remained illiterate and was not employed.
(v) The condition of Sakal and his family became better whereas Vilas and his family lived in poverty.
Question 2. Visit a nearby village or a slum area and write down a case study of a boy or girl of your age facing the same condition as Vilas or Sakal.
Answer A typical case study can be written as follows:
I visited my ancestral village and found some families in a similar plight to Vikas. One boy, Puran, who is 15 years old, works as a farm labourer. In fact, all his family members are farm labourers, as they are landless and uneducated. Since there is no secondary school in the village, Puran did not study beyond class five.
He does not have enough clothes and whatever clothes he is wearing are also torn and worn out with use. He and his family members are undernourished. His father has already become a patient of tuberculosis and may not live long. He feels he will forever remain a poor person.
Page 19
Question 1. Based on the picture can you classify these activities into three sectors?
AnswerThe photo at top is depicting agriculture, which is a primary sector activity.
The photo in the middle is depicting manufacturing, which is a secondary sector activity.
The photo at bottom is depicting shipping, which is a tertiary sector activity.
Page 20
Question 1. Say whether these activities are economic or non-economic activities
(a) Vilas sells fish in the village market.
Answer Economic activity.
(b) Vilas cooks food for his family.
Answer Non-economic activity
(c) Sakal works in the private firm.
Answer Economic activity
(d) Sakal looks after his younger brother and sister.
Answer Non-economic activity
Page 21
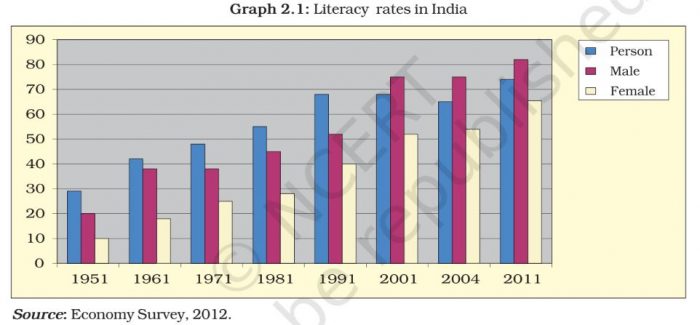
Question 1. Study the graph and answer the following question.
(a) Has the literacy rates of the population increased since 1951?
Answer Yes the literacy rates of the population have increased since 1951 as shown below.
| Literacy in 1951 | Literacy in 2001 |
| Male-28 | Male-75 |
| Female-11 | Female-52 |
(b) In which year India has the highest literacy rates?
Answer India has the highest literacy rates in 2001.
(c) Why literacy rate is high among the males of India?
Answer India traditionally has a patriarchal male dominated society where more importance is given to males.
Culturally due to division of labour the males go out of their homes and get better access to education.
Poor families due to monetary constraints prefer to send only their sons to school and not their daughters.
(d) Why are women less educated than men.
Answer Women are less educated than men because more preference is given to the boys or sons in the family for education as they are considered as future of the family.
Traditionally, the girls were expected to stay at home and look after domestic chores. So, education among girls was not encouraged. Because of the above reasons the women are less educated than men.
(e) How would you calculate literacy rate in India?
Answer The literacy rate can be calculated on the basis of the formula i.e., the number of literate people divided by the population multiplied by 100.
(f) What is your projection about India’s literacy rate in 2010?
Answer The projection about India’s literacy rate in year 2010 would be between 75% to 85%.
Page 22
Question 1. Count the number of boys and girls studying in your class or in your neighbouring co-ed school. Ask the school administrator to provide you with the data of boys and girls studying in your class below five years and ten years. Study the difference if any and explain it in the classroom.
Answer Most likely you will find that the proportion of girls in comparison to boys goes down in the older age group compared to the younger age group. This shows that the dropout rate of girls from school is more than that of boys. The reasons are similar to the ones already discussed in the matter of literacy, with one added reason that in some families, girls are kept back from school to help in the domestic chores due to poor health or non-availability of the mother.
Page 23
Question 4. (a)
| Year | Number of colleges | Number of universities | Students | Teachers |
| 1950-1951 | 750 | 30 | 263000 | 24000 |
| 1990-1991 | 7346 | 177 | 4925000 | 272000 |
| 1996-1997 | 9703 | 214 | 6755000 | 321000 |
| 1998-1999 | 11089 | 238 | 7417000 | 342000 |
Table 2.1: Number of Institutions of Higher Education, Enrolment and Faculty
Discuss this table in the classroom and answer the following question
Is the increase in number of colleges adequate to admit the increasing number of students?
Answer No, the increase in the number of colleges is not adequate to admit the increasing number of students because the number of students is increasing at a faster rate compared to the colleges being established.
(b) Do you think we should have more number of universities?
Answer Seeing the ever increasing number of students, we should establish more universities to cater to their needs. But at the same time greater stress should be on opening more and more colleges.
(c) What is the increase noticed among the teachers in the year 1998-99?
Answer There was an increase of 21 thousand teachers in the year 1998-99 compared to 1998-99?
(d) What is your idea about future colleges and universities?
Answer In future colleges and universities, stress should be on vocationalisation of education.
There should also be a focus on distance education, and convergence of formal and informal, distance and IT education institutions.
Colleges should be set up in rural areas to benefit the rural students.Colleges and universities should focus on providing student centered education.
Page 23
Question 1. Table 2.2 Health infrastructure over the years
| 1951 | 1981 | 2001 | |
| SC/ PHC / CHC | 725 | 57363 | 163181 |
| Dispensaries and Hospitals | 9209 | 23555 | 43322 |
| Beds | 117198 | 569495 | 870161 |
| Doctors | 61800 | 268700 | 503900 |
| Nursing Personnel | 18054 | 143887 | 737000 |
SC : Sub Center,
PHC : Primary Health Center
CHC : Community Health Center
Study the table 2.2 and answer the following questions.
(a) What is the percentage increase in dispensaries from 1951 to 2001?
Answer (a) The percentage increase in dispensaries and hospitals from 1951 to 2001 is
(b) What is the percentage increase in doctors and nursing personnel from 1951 to 2001?
Answer (b) (i) The percentage increase in doctors from 1951 to 2001 is
(ii) Percentage increase in nursing personnel is
(c) Do you think the increase in the number of doctors and nurses is adequate for India? If not, why?
Answer (c) No, the increase in the number of doctors and nurses is inadequate because the ratio of both doctors and nursing personnel is still too low for India’s population.
(d) What other facilities would you like to provide in a hospital?
Answer (d) Other facilities we would like to provide in a hospital
(i) Hospitals should be spotlessly clean and hygienic.
(ii) Emergency wards and ambulances should be there in all hospitals.
(iii) Doctors should be available 24 hours.
(iv) Chemist shop should be available inside the hospitals.
(v) Documentation for OPD as well as inpatients should be reduced to the minimum.
(e) Discuss about the hospital you have visited.
Answer (e) I have visited the Anand Hospital in our city
(i) It is a 200 bed multi speciality hospital and provides high class medical facilities.
(ii) It has state of the art operation theatres and a blood bank.
(iii) It has various machines to carry out different kinds of tests like ultrasound, MRI, etc.
(iv) It has a well equipped pathology lab.
(v) It has a number of specialists in different branches of medicine.
(vi) It caters to the needs of the entire city and also to the surrounding rural areas.
(vii) It is centrally air conditioned. It also has a medical store.
(viii) The only drawback is that being a private hospital the treatment for the patients is costly.
Exercises
Question 1. What do you understand by ‘people as a resource?
Answer ‘People as a resource’ is a way of referring to a country’s working people in terms of their existing productive skills and abilities. Because the humans contribute to GDP, they are also considered as a resource.
Question 2. How is human resource different from other resources like land and physical capital?
Answer (i) Land, water, forests and minerals are resources which are essential for the growth, progress and development of human society
(ii) However these resources become usable only when the human being processes them and develops them; otherwise they are of use on their own. Without human beings these resources would remain unutilised. Thus human resource is the most importance resource because it helps to utilise natural resources.
Question 3. What is the role of education in human capital formation?
Answer Education plays a significant and very vital role in human capital formation because education helps the humans to achieve and realise their full potential and achieve success in life in the form of higher incomes earned through better jobs and higher productivity. Education helps the people by broadening their knowledge and providing them training.
Question 4. What is the role of health in human capital formation?
Answer Health plays an important role in human capital formation for the following reasons
(i) Only a healthy person can perform to his full potential.
(ii) A healthy person can do the work in a more effective manner.
(iii) A healthy person can contribute to the growth and development of the economy by doing productive work.
(iv) An unhealthy person becomes a liability for an organisation. Indeed health is an indispensable basis for realising one’s well being. Realising the importance of health, improvement in the health status of the population has been the priority of the government.
Question 5. What part does health play in the individual’s working life?
Answer Health plays an important part in the individual’s working because
(i) An unhealthy person cannot work efficiently.
(ii) If the body is healthy then only the mind can perform well.
(iii) A healthy person is able to work harder and better, thus earning more and living a better life.
Question 6. What are the various activities undertaken in the primary sector, secondary sector, and tertiary sector?
Answer Primary Sector Activities Agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, fishing, poultry farming and mining.
Secondary Sector Activities Include manufacturing and construction.
Tertiary Sector Activities Trade, transport, communication, banking. education, health, tourism, services, insurance, etc.
Question 7. What is the difference between economic activities and non-economic activities?
Answer The activities which are performed for money and results in economic income are called economic activities. These activities add value to the national income.
Those activities which are not performed for money and do not result in economic income are called non-economic activities
Question 8. Why are women employed in low paid work?
Answer A majority of the women in India have very less education and low skill formation and thus they perform mainly unskilled labour and get lower wages.
(i) Being less educated they are unaware of their rights and about minimum wages, or they work in the unorganised sector where they get low wages.
(iii) They are traditionally considered physically inferior to men and believed to do less work, so they are paid less compared to men.
Question 9. How will you explain the term unemployment?
Answer Unemployment is said to exist when people who are willing to Work at the current wages cannot find jobs.
Question 10. What is the difference between disguised unemployment and seasonal unemployment?
Answer Disguised Unemployment
(i) In case of disguised unemployment, people appear to be employed but are actually not employed.
(ii) Sometimes in agricultural families, eight people are working in the farm, whereas only five people are needed to do that work. Thus three persons are surplus and they are not needed on the farm. They also do not help to increase the production of the farm.
(iii) If these three extra persons are removed from the farm, the production from the farm will not decrease; therefore these three persons appear to be employed but are actually disguisedly unemployed.
Seasonal Unemployment
(i) Seasonal unemployment happens when people are not able to find jobs during some months of the year.
(ii) People dependent upon agriculture usually face such a kind of problem. There are certain busy seasons when sowing, harvesting weeding and threshing is done. But when the plants are growing there is not much work.
(iii) During this period, they remain unemployed and are said to be seasonally unemployed.
Question 11. Why is educated unemployed a peculiar problem of India?
Answer
(i) In the case of urban areas, educated unemployment has become a common phenomenon. Many urban youth with matriculation, graduation and post graduation degrees are not able to find jobs.
(ii) A study showed that unemployment of graduates and post graduates has increased faster than among matriculates.
(iii) A paradoxical manpower situation is witnessed as surplus of manpower in certain categories coexists with shortage of manpower in others.
(iv) There is unemployment among technically qualified persons on one hand, while there is dearth of technical skills required for economic growth.
(v) So we can say that educated unemployment is indeed a peculiar problem of India.
Question 12. In which field do you think India can build the maximum employment opportunity?
Answer (i) Agriculture sector in India is suffering from disguised unemployment and there is no more possibility of further employment.
(ii) Unemployed rural labour force is now migrating to the cities to work in the industrial sector where many industries have been set up and has the maximum capacity to provide employment.
(iii) The educated unemployed can also find jobs in the service sector or the tertiary sector.
Question 13. Can you suggest some measures in the education system to mitigate the problem of the educated unemployed?
Answer Vocational education should be encouraged so that after education, people do not have difficulty in getting jobs because they will better trained for work,
(i) More use of Information technology (IT) should be made in giving education.
(ii) Education should cater to the needs of the employment markets.
(iii) More opportunities should be made available in the tertiary sector where more educated unemployed people can find jobs.
Question 14. Can you imagine some village which initially had no job opportunities but later came up with many?
Answer Rampur was a small village which initially depended on agriculture which was also dependent on rainfall.
(i) Then electricity reached the village and people could irrigate their fields and could grow 2 to 3 crops in a year and get work.
(ii) Some people set up small scale industries which could be run by electricity and provided employment to people.
(iii) A school was established and now the population started to become educated and as a result they could seek employment in and outside the village. The village became prosperous and soon had better health, education, transport and job facilities.
Question 15. Which capital would you consider the best land labour physical capital and human capital? Why?
Answer
(i) Land labour physical capital and human capital are very important for the growth and development of the society and the economy.
(ii) In the absence of any of these resources we cannot hope to much progress, so they are very important.
(iii) However, human capital is the most important capital because all other types of capital can be utilised only by humans; if humans do not develop and process other capital or resources and make them usable, they would remain underdeveloped and unutilised because on their own they are useless and of no use to anybody.
If we develop human capital, all others will automatically develop and lead to progress.
Thank you for this ☺☺☺
I appreciate your effort and I am helped. Thank you a lot.
It is very helpful.
Thank you mam. Answers were really helpful
Thank you maa’m answers were really helpful
It clears my doubt this is helpful for me