Class 9 Science Chapter 5
The Fundamental Unit of Life NCERT Solutions
Page 59
1. Who discovered cells, and how?
Answer:
Cells were discovered in 1665 by an English Botanist, Robert Hooke. He used a primitive microscope to observe cells in a cork slice.
2. Why is the cell called the structural and functional unit of ?
Answer:
Cell is the smallest unit of life and is capable of all living functions. All the living organism are made up cells and also all the processes taking place inside the body of organism are performed by cells. All cells vary in their shape, size, and activity they perform. In fact, the shape and size of the cell is related to the specific functions they perform. Cells are the building blocks of life. This is the reason why cells are referred to as the basic structural and functional units of life.
Page 61
1. How do substances like CO2 and water move in and out of the cell? Discuss.
Answer:
Movement of Carbon dioxide
Diffusion is the spontaneous movement of molecules from the region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Concentrations of carbon dioxide is high inside the cell whereas the concentration of CO2 is low outside the cell. Therefore, by the process of diffusion, CO2 moves from a region of higher concentration (inside the cell) towards a region of lower concentration (outside the cell).
Movement of water
The passage of water from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration through semi-permeable membrane is called as osmosis.
Water moves from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration through the plasma membrane. However, the movement of water across the plasma membrane of the cell is affected by the
amount of substance dissolved in water.
2. Why is the plasma membrane called a selectively permeable membrane?
Page 63
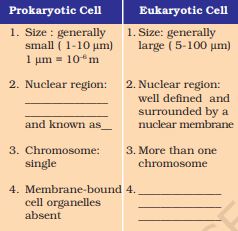
1. Fill in the gaps in the following table illustrating differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Answer:
| Prokaryotic Cell | Eukaryotic Cell |
| 1 Size: Generally small ( 1-10 µ) 1 µm = 10-6m | 1 Size: generally large (5 – 100 µm) |
| 2 Nuclear region : poorly defined because of the absence of a nuclear membrane, and is know as nucleoid. | 2 Nuclear region: well- defined and surrounded by a nuclear membrane. |
| 3 Chromosome : single | 3 More than one chromosome. |
| 4 Membrane bound cell organelles are absent. | 4 Membrane-bound cell organelles such as mitochondria, plastids etc are present. |
Page 65
1. Can you name the two organelles we have studied that contain their own genetic material?
Answer:
Mitochondria and plastids are the two organelles that contain their own genetic material.
2. If the organisation of a cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence, what will happen?
Answer:
Cell is the smallest unit of life which is capable of performing all the basic functions. If the organisation of a cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence then cell will not be able to perform the basic functions like respiration, nutrition, excretion etc. All the life processes will stop and it may result in death.
3. Why are lysosomes known as suicide bags?
Answer:
They are simple tiny spherical sac like structures evenly distributed in the cytoplasm.
Each lysosome is a small vesicle surrounded by a single membrane and contains enzymes. They remove worn out and poorly working cellular organelles by digesting them to make way for their new replacements. They are called suicide bags of cell. During break down of cell structure, when cell gets damaged, lysosomes may burst and enzymes eat up their own cells.
4. Where are proteins synthesised inside the cell?
Answer:
Ribosomes are very small structures found either in a free state, suspended in the cytoplasm, or attached to the surface of the endoplasmic reticulum. Ribosomes are the site for protein synthesis.
Exercise Page 67
1. Make a comparison and write down ways in which plant cells are different from animal cells.
Answer:
| Animal Cell | Plant Cell |
| Animal cells are generally small in size. | Plant cell are larger than animal cells. |
| Except protozoan Euglena no animal cell possess plastids. | Plastids are present. |
| Cell wall is absent. | The plasma membrane of plant cell is surrounded by a rigid cell wall of cellulose. |
| Cell wall is absent. | The plasma membrane of plant cell is surrounded by a rigid cell wall of cellulose. |
| Cell wall is absent. | The plasma membrane of plant cell is surrounded by a rigid cell wall of cellulose. |
| Cell wall is absent. | The plasma membrane of plant cell is surrounded by a rigid cell wall of cellulose. |
2. How is a prokaryotic cell different from a eukaryotic cell?
Answer:
| Prokaryotic cell | Eukaryotic cell |
| They are unicellular | They are multicellular. |
| Size of the cell is generally small | Size of the cell is generally large |
| It contains single chromosome | It contains more than one chromosome |
| Nucleolus is absent. | Nucleolus is present. |
| Membrane bound cell organelles are absent | Membrane bound cell organelles are present |
| Nuclear region is poorly defined due to absence of
nuclear membrane. |
Nuclear region is well defined and is surrounded by
nuclear membrane |
| For Ex: blue green algae, bacteria | For Ex: fungi, plants, animals |
3. What would happen if the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down?
Answer:
Plasma membrane regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell by the process of diffusion or osmosis.If the plasma membrane ruptures or break down , then the cell will die.The internal composition of the cell will be lost and it will not be able to perform the basic functions.The cell will not be able to exchange the material with the surrounding.
4. What would happen to the life of a cell if there was no Golgi apparatus?
Answer:
They are involved in synthesis of cell wall, plasma membrane and lysosomes. It produces vacuoles which contain cellular secretions eg: enzymes, protein, cellulose etc. They act as an area for storage, processing and packaging of various cellular secretions.
If golgi apparatus is not present in cell then all these functions will not be possible.
5. Which organelle is known as the powerhouse of the cell? Why?
Answer:
Mitochondria are tiny bodies of varying shape(cylindrical, rod-like, spherical)distributed in cytoplasm. Each mitochondria is surrounded by double membrane. Outer membrane is porous. Inner membrane has folds and therefore have large surface area. They uses oxygen to oxidise carbohydrates and fats present in the cell to carbon dioxide and water. Oxidation releases energy, a portion of which is used to form ATP.
Since mitochondria synthesises energy rich compound ATP it is called powerhouse of cell.
ATP is called energy carrier or energy currency of the cell.
6. Where do the lipids and proteins constituting the cell membrane get synthesised?
Answer:
Lipids are synthesised in Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum(SER) and proteins are synthesised in Rough Endoplasmic reticulum(RER)
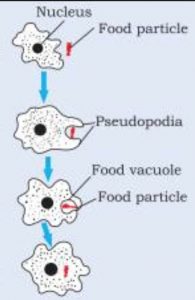
7. How does an Amoeba obtain its food?
Answer:
Amoeba takes in food using temporary finger-like extensions of the cell surface which fuse over the food particle forming a food-vacuole . Inside the food vacuole, complex substances are broken down into simpler ones which then diffuse into the cytoplasm.
8. What is osmosis?
Answer:
The diffusion of water or solvent from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration through a semi permeable membrane is called osmosis.
9. Carry out the following osmosis experiment:
Take four peeled potato halves and scoos each one out to make potato cups. One of these potato cups should be made from a boiled potato. Put each potato cup in a trough containing water. Now,
(a) Keep cup A empty
(b) Put one teaspoon sugar in cup B
(c) Put one teaspoon salt in cup C
(d) Put one teaspoon sugar in the boiled potato cup D. Keep these for two hours. Then observe the four potato cups and answer the following:
(i) Explain why water gathers in the hollowed portion of B and C.
(ii) Why is potato A necessary for this experiment?
(iii) Explain why water does not gather in the hollowed out portions of A and D.
Answer:
1) Water gathers in the hollowed portion of B and C because water enters the potato as a result of osmosis. Since the medium surrounding the cell has a higher water concentration than the cell, the water moves inside by osmosis.
2) Potato A in the experiment acts a control set up. No water gathers in the hollowed portion of potato A.
3) Water does not gather in the hollowed portion of potato A because potato cup A is empty. It is a control set up in the experiment.
Water is not able to enter potato D because potato used here is boiled. Boiling denatures the protein present in the cell membrane and thus disrupts the cell membrane. For osmosis semipermeable membrane is required which is disrupted in this case. Therefore osmosis will not occur. Hence water does not enter the boiled potato cup.
Leave a Reply