Class 8 Science Chapter 1 |
Crop Production and Management NCERT Solutions
1. Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks.
float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation
(a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called _________.
(b) The first step before growing crops is _____________ of the soil.
(c) Damaged seeds would _____________ on top of water.
(d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and _____________ and _____________ from the soil are essential.
Answer:
(a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called crop.
(b) The first step before growing crops is perpetration of the soil.
(c) Damaged seeds would float on top of water.
(d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and water and nutrients from the soil are essential.
2. Match items in column A with those in column B.
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) Kharif crops | (1) Food for cattle |
| (b) Rabi crops | (2) Urea and super phosphate |
| (c) Chemical fertilizers | (3) Animal excreta, cow dung, urine and plant waste |
| (d) Organic manure | (4) Wheat, gram, pea |
| (5) Paddy and maize |
Answer:
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) Kharif crops | (5) Paddy and maize |
| (b) Rabi crops | (4) Wheat, gram, pea |
| (c) Chemical fertilizers | (2) Urea and super phosphate |
| (d) Organic manure | (3) Animal excreta, cow dung, urine and plant waste |
3. Give two examples of each:(a) Kharif crop
(b) Rabi crop
Answer: (a) Maize and rice
Answer: (b) Mustard and wheat
4. Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following.
(a) Preparation of soil
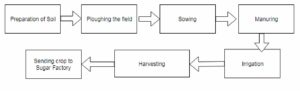
Answer: The soil is prepared for sowing the seeds of the crop by ploughing, levelling and manuring. The process of loosening and turning of soil is called ploughing. Ploughing of fields is done by using an implement called plough. The loosening of soil by ploughing is beneficial because the loose soil allows the plant roots to penetrate freely and deeply into the soil so that plants are held more firmly to the ground, allows the roots of plants to breathe easily, help in the growth of worms and microbes present in the soil, uproots and buries weeds standing in the field. The ploughed soil is levelled by pressing it with a wooden leveller so that the top soil is not blown away by wind or drained off by water. The levelling of ploughed soil is beneficial because it prevents the top fertile soil from being carried away by strong winds or washed away by rain water, helps in the uniform distribution of water in the fields during irrigation, helps in preventing the loss of moisture. The levelling of ploughed soil in the field is done by using an implement called leveller. Manuring is done to in increase the fertility of the soil before seeds are sown in it.
(b) Sowing
The process of scattering seeds in the ground soil for growing the crop plants is called sowing. There are two methods of sowing the seeds in the soil. These are sowing by hand, sowing with a seed drill. In sowing by hand seeds are taken in hand and gradually scattered in the entire ploughed field. In this method there is no proper spacing or proper depth at which seed are sown. The seeds scattered on the surface of the soil for sowing can be picked up and eaten by the bird. The seed drill is tied to back of the plough and seeds are put into the funnel of the seed drill. As the plough makes furrows in the soil, the seed from seed drill are gradually released and sown into the soil. In this method the seeds are sown at the correct depth and correct interval, cannot be picked up and eaten by the birds, saves time and labour. In sowing , the seeds should be sown at right depth in the soil, sown at right interval or spacing, should not be sown in a dry soil, should not be sown in a highly wet soil.
(c) Weeding
The unwanted plants which grow along with a cultivated crop are called weed. The examples of weeds areWild oat, grass, amaranthus, chenopodium etc. The process of removing weeds from a crop field is called weeding. Weeding is necessary because weeds compete with crop plant for water, sunlight, nutrients, space and hence affect plant growth. Weeds are removed by pulling them out with hand ,by using a trowel or by spraying weedicides. The weedicides kill the weeds but do not damage the main crop.
(d) Threshing
Separation of grains from harvested crop is called threshing. Threshing is done by threshing machine or by cattle. Cattle are tied in a series around a pole. Harvested crop is spread around the pole. Animals are made to trample the harvested crop. It helps in separating the grains from the harvested crop.
5. Explain how fertilisers are different from manure.
Answer:
| Manures | Fertilisers |
| It is a natural substance obtained by decomposition. | A chemical fertiliser is a salt or an organic compound |
| A manure is not very rich in essential plant nutrients. | Fertilisers are rich in plant nutrient like nitrogen, phosphorus or potassium. |
| A manure provide a lot of humus to the soil. | Fertiliser does not provide any humus to the soil. |
| A manure is absorbed slowly by the plant. | They are easily absorbed by the plants. |
| They can be prepared in the fields. | They are prepared in factories. |
6. What is irrigation? Describe two methods of irrigation which conserve water.
Answer: The process of supplying water to crop plant in the fields is called irrigation.
The two methods of irrigation which conserve water are:
1)Sprinkler system: A main pipeline is laid in the field. Perpendicular pipes having rotating nozzles at the top are joined to the main pipelines at regular intervals. When water from a tube-well is allowed to flow through the main pipelines under pressure with the help of a pump, it escapes from the rotating nozzles. This water gets sprinkled on the crop plants as if it is raining.
Advantages
1)It is more useful for the uneven land where sufficient water is not available.
2)It is very useful for sandy soil.
Drip system
There is network of narrow pipes with small holes in the fields. When water flows through the narrow pipes, it fall drop by drop at the position of roots of the plants. This water is absorbed by the soil in the root zone of the plants and utilised by the plant. There is no wastage of irrigation of water.
Advantages
1)It provides water to plants drop by drop.So water is not wasted at all.
2) It minimises the use of water in agriculture. It is useful in those regions where the availability of water is poor.
7. If wheat is sown in the kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
If wheat is sown in the kharif season, it will not grow well. This is because wheat plants cannot tolerate too much water of the rainy season.
8. Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Plants require good nutrients for their proper growth and functioning activities. When a farmer continuously grows crops one after the other instantly, then all nutrients available in the soil gets reduced i.e. there will not be sufficient amount of nutrients, and the total crop production or the yield gets reduced automatically. This makes the soil poor in certain nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, etc.
9. What are weeds? How can we control them?
The unwanted plants which grow along with a cultivated crop are called weed. The example of weeds are wild oat, grass, Amaranthus, chenopodium etc. The process of removing weeds from a crop field is called weeding.
methods to control weeds are :
1 Weeds can be controlled by using weedicides. The poisonous chemicals which are used to kill weeds in the fields are called as weedicides. The weedicides kill the weeds but do not damage the main crop.
2 Tilling before sowing of crops also removes weeds.
3 Removing weeds manually using khurpa
For Example : 2,4-D, MCPA, Butachlor etc.
10. Arrange the following boxes in proper order to make a flow chart of the sugarcane crop production.
Answer:
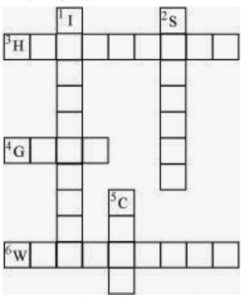
11. Complete the following word puzzle with the help of clues given below.
Down
1.Providing water to the crops.
2. Keeping crop grains for a long time under proper condition.
5. Certain plants of the same kind grown on a large scale.
Across
3. A machine used for cutting the matured crop.
4. A rabi crop that is also one of the pulses.
6. A process of separating the grain from chaff.
Answer:


very nice, was waiting for question answer section on this portal.