| Exercise 11.1 Exercise 11.2 Exercise 11.3 Exercise 11.4 Exercise 11.5 |
NCERT Answers for Class 6 Maths Chapter 11 |
Algebra Exercise 11.2
Page 230
Ex 11.2 Class 6 Maths Question 1. The side of an equilateral triangle is shown by l. Express the perimeter of the equilateral triangle using l.
Answer
Side of equilateral triangle = l
Perimeter = l + l + l
= 3l
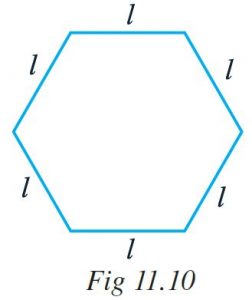
Ex 11.2 Class 6 Maths Question 2. The side of a regular hexagon (Fig 11.10) is denoted by l. Express the perimeter of the hexagon using l. (Hint : A regular hexagon has all its six sides equal in length.)
Answer
Side of a regular hexagon = l
Perimeter = l + l + l + l + l + 1
= 6l
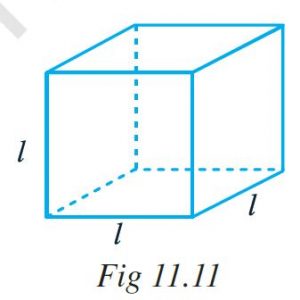
Ex 11.2 Class 6 Maths Question 3. A cube is a three-dimensional figure as shown in Fig 11.11. It has six faces and all of them are identical squares. The length of an edge of the cube is given by l. Find the formula for the total length of the edges of a cube.
Answer
Length of an edge of the cube = l
Number of edges = 12
Total length of the edges = Number of edges × length of an edge
=12l
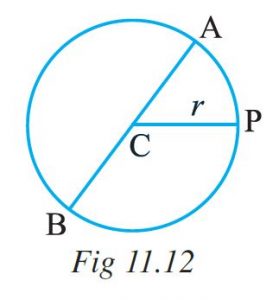
Ex 11.2 Class 6 Maths Question 4. The diameter of a circle is a line which joins two points on the circle and also passes through the centre of the circle. (In the adjoining figure (Fig 11.12) AB is a diameter of the circle; C is its centre.) Express the diameter of the circle (d) in terms of its radius (r).
Answer
Diameter = AB
= AC + CB
= r + r
= 2r
Hence, the diameter of the circle in terms of its radius is 2r
Ex 11.2 Class 6 Maths Question 5. To find sum of three numbers 14, 27 and 13, we can have two ways:
(a) We may first add 14 and 27 to get 41 and then add 13 to it to get the total sum 54 or
(b) We may add 27 and 13 to get 40 and then add 14 to get the sum 54. Thus, (14 + 27) + 13 = 14 + (27 + 13)
This can be done for any three numbers. This property is known as the associativity of addition of numbers. Express this property which we have already studied in the chapter on Whole Numbers, in a general way, by using variables a, b and c.
Answer
For any three whole numbers a, b and c
(a + b) + c = a + (b + c)
Leave a Reply