Page 61
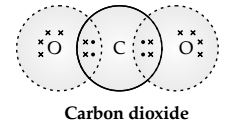
Question 1. What would be the electron dot structure of carbon dioxide which has the formula CO2?
Answer 1 Electron dot structure of CO2:
Atomic number of carbon (C) = 6
Electronic configuration of carbon (C) = 2, 4
Valence electrons of carbon (C) = 4
Atomic number of oxygen (O) = 8
Electronic configuration of oxygen (O) = 2, 6
Valence electrons of oxygen (O) = 6
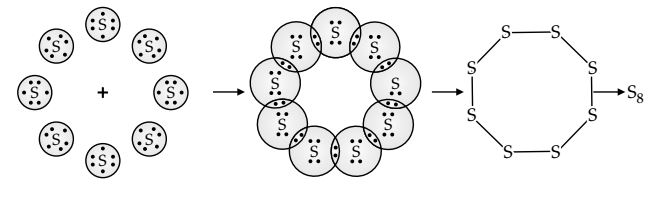
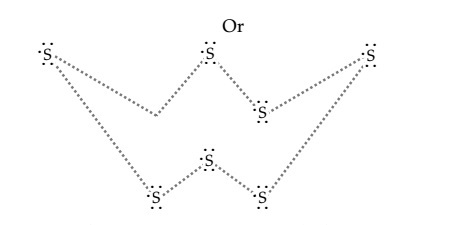
Question 2. What would be the electron dot structure of a molecule of sulphur which is made up of eight atoms of sulphur? (Hint – The eight atoms of sulphur are joined together in the form of a ring.)
Answer 2 : Electron dot structure of a sulphur molecule
Atomic number of sulphur (S) = 16
Electronic configuration of sulphur (S) = 2, 8, 6
Valence electrons of sulphur (S) = 6
Page 68-89
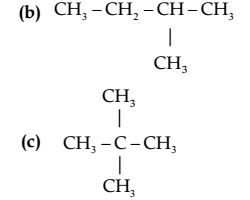
Question 1. How many structural isomers can you draw for pentane?
Answer 1 Three structural isomers are possible for pentane.
(a) CH3 – CH2– CH2 – CH2 – CH3
Question 2. What are the two properties of carbon which lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we see around us?
Answer 2: The two properties of carbon which give rise to a large number of compounds are
(i) Catenation: It is the ability to form bonds with other atoms of carbon. The compounds may have long chains of carbon, branched chains of carbon or even carbon atoms arranged in rings. Also the carbon atoms may be linked by single, double or triple bonds.
(ii) Tetravalency: With the valency of four, carbon is capable of bonding with four other atoms. A carbon atom has four valence electrons. So, it has an ability to bond with four other atoms of carbon or atoms of any other monovalent element.
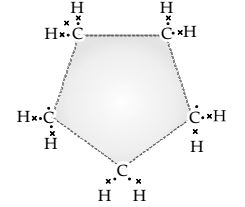
Question 3. What will be the formula and electron dot structure of cyclopentane?
Answer 3: The formula for cyclopentane is C5H10. Its electron dot structure is given below.
Question 4. Draw the structures for the following compounds.
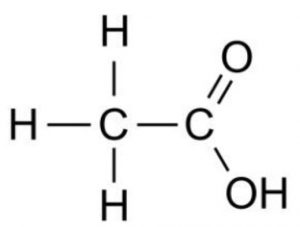
(i) Ethanoic acid
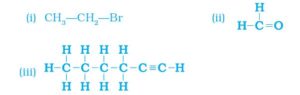
(ii) Bromopentane
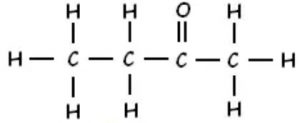
(iii) Butanone
(iv) Hexanal
Are structural isomers possible for bromopentane?
Answer 4
(i) Ethanoic acid
CH3COOH
(ii) Bromopentane
(iii) Butanone
CH3CH2COCH3
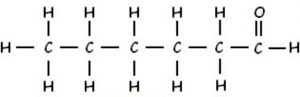
(iv) Hexanal
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CHO
Question 5. How would you name the following compounds?
Answer 5
(i) Bromoethane
(ii) Methanal
(iii) Hexyne
Page 71
Question 1. Why is the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid an oxidation reaction?
Answer 1 Since the conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid involves the addition of oxygen, therefore it is an oxidation reaction.
CH3CH2OH ——-> CH3COOH
Question 2. A mixture of oxygen and ethyne is burnt for welding. Can you tell why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used?
Answer 2 2HC ≡ CH + 5O2 → 4CO2 + 2H2O + Heat
When ethyne is burnt in air, it gives a sooty flame. This is due to incomplete combustion caused by limited supply of air. However, if ethyne is burnt with oxygen, it gives a clean flame with temperature 3000°C because of complete combustion. This oxy-acetylene flame is used for welding. It is not possible to attain such a high temperature without mixing oxygen. This is the reason why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used.
Page 74
Question 1. How would you distinguish experimentally between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid?
Answer 1 We can distinguish between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid on the basis of their reaction with carbonates and hydrogen carbonates.
Acid reacts with carbonate and hydrogen carbonate to evolve CO2 gas that turns lime water milky.
Metal Carbonate/Hydrogencarbonate+Carboxylic acid —-> Salt+Water+Carbon dioxide
Alcohols, on the other hand, do not react with carbonates and hydrogen carbonates.
Question 2. What are oxidising agents?
Answer 2 Some substances such as alkaline potassium permanganate and acidified potassium dichromate are capable of adding oxygen to others. These are known as oxidising agents.
Page 76
Question 1. Would you be able to check if water is hard by using a detergent?
Answer 1 Detergents are ammonium or sulphonate salts of long chain carboxylic acids. Unlike soap, they do not react with calcium and magnesium ions present in hard water to form scum. They give a good amount of lather irrespective of whether the water is hard or soft. This means that detergents can be used in both soft and hard water. Therefore, it cannot be used to check whether the water is hard or not.
Question 2. People use a variety of methods to wash clothes. Usually after adding the soap, they ‘beat’ the clothes on a stone, or beat it with a paddle, scrub with a brush or the mixture is agitated in a washing machine. Why is agitation necessary to get clean clothes?
Answer 2 A soap molecule has two parts namely hydrophobic and hydrophilic. With the help of these, it attaches to grease or dirt particles and form a cluster called micelle.These micelle remain suspended as a colloid. To remove these micelle, it is necessary to agitate clothes.
Page 77
Question 1. Ethane, with the molecular formula C2H6 has
(a) 6 covalent bonds.
(b) 7 covalent bonds.
(c) 8 covalent bonds.
(d) 9 covalent bonds.
Answer 1: (b) 7 covalent bonds.
Ethane has 7 covalent bonds. One bond is between two carbon atoms and rest of the six are between hydrogen atoms.
Question 2. Butanone is a four-carbon compound with the functional group
(a) carboxylic acid.
(b) aldehyde.
(c) ketone.
(d) alcohol.
Answer 2: (c) ketone
The functional group of butanone is ketone.
Question 3. While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, it means that
(a) the food is not cooked completely.
(b) the fuel is not burning completely.
(c) the fuel is wet.
(d) the fuel is burning completely.
Answer 3: (b) the fuel is not burning completely
While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, then it means that the fuel is not burning completely.
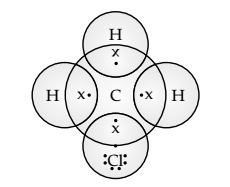
Question 4. Explain the nature of the covalent bond using the bond formation in CH3Cl.
Answer 4 Carbon completes its octet by sharing its four electrons with other carbon atoms or with atoms of other elements, because losing and gaining of four electrons requires extra amount of energy which makes the system unstable. In covalent bonding, both the atoms share the valence electrons, that is, the shared electrons belong to the valence shells of both the atoms.
Here, carbon requires 4 electrons to complete its octet, while each hydrogen atom requires one electron to complete its duplet. Also, chlorine requires an electron to complete the octet. Therefore, all of these share the electrons and as a result, carbon forms 3 bonds with hydrogen and one with chlorine.
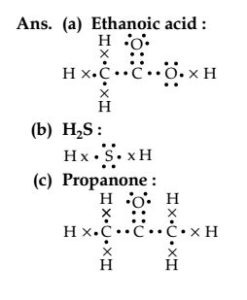
Question 5. Draw the electron dot structures for
(a) ethanoic acid.
(b) H2S.
(c) propanone.
(d) F2
Question 6. What is an homologous series? Explain with an example.
Answer 6 A series of compounds in which the same functional group substitutes for hydrogen in a carbon chain is called a homologous series.
In this series carbon atoms can be linked together to form chains of varying lengths. In addition, hydrogen atom or atoms on these carbon chains can be replaced by any of the functional groups. The presence of a functional group such as alcohol dictates the properties of the carbon compound, regardless of the length of the carbon chain.
For example: methane, ethane, propane, butane, etc. are all part of the alkane homologous series.
The general formula of this series is CnH2n+2.
Methane — CH4
Ethane — CH3CH3
Propane — CH3CH2CH3
Butane — CH3CH2CH2CH3
Question 7. How can ethanol and ethanoic acid be differentiated on the basis of their physical and chemical properties?
Answer 7 Ethanol is a liquid at room temperature with a pleasant odour while ethanoic acid has vinegar like smell. The melting point of ethanoic acid is 17°C. This is below room temperature and hence, it freezes during winters.
Ethanoic acid reacts with metal carbonates and metal hydrogen carbonates to form salt, water, and carbon dioxide gas while ethanol does not react with them.
Metal Carbonate/Hydrogen carbonate+Carboxylic acid → Salt+Water+Carbon dioxide
2CH3COOH+Na2CO3→2CH3COONa+H2O+CO2
Metal Carbonates/Metal Hydrogen carbonates + Alcohols → No reaction
CH3CH2OH+Na2CO3 → No reaction
Question 8. Why does micelle formation take place when soap is added to water? Will a micelle be formed in other solvents such as ethanol also?
Answer 8 Soap molecule has two ends. One end is hydrophilic and another end is hydrophobic. When soap is dissolved in water and clothes are put in the soapy solution, soap molecules converge in a typical fashion to make a structure; called micelle. The hydrophobic ends of different molecules surround a particle of grease and make the micelle; which is a spherical structure. In this, the hydrophilic end is outside the sphere and hydrophobic end is towards the centre of the sphere. This is why micelle formation takes place when soap is added to water. Micelle is not formed in other solvent such as ethanol.
Question 9. Why are carbon and its compounds used as fuels for most applications?
Answer 9 Most of the carbon compounds give a lot of heat and light when burnt in air. Saturated hydrocarbons burn with a clean flame and no smoke is produced. The carbon compounds, used as a fuel, have high calorific values. Therefore, carbon and its compounds are used as fuels for most applications.
Question 10. Explain the formation of scum when hard water is treated with soap.
Answer 10 Soap does not work properly when the water is hard. A soap is a sodium or potassium salt of long chain fatty acids. Hard water contains salts of calcium and magnesium. When soap is added to hard water, calcium and magnesium ions present in water displace sodium or potassium ions from the soap molecules forming an insoluble substance called scum. A lot of soap is wasted in the process.
Question 11. What change will you observe if you test soap with litmus paper (red and blue)?
Answer 11 Since soap is basic in nature, it will turn red litmus blue. However, the colour of blue litmus will remain blue.
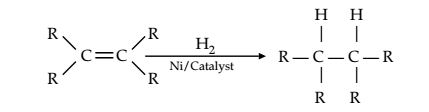
Question 12. What is hydrogenation? What is its industrial application?
Answer 12 Hydrogenation is the process of addition of hydrogen. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are added with hydrogen in the presence of palladium and nickel catalysts to give saturated hydrocarbons.
This reaction is applied in the hydrogenation of vegetables oils, which contain long chains of unsaturated carbons.
Question 13. Which of the following hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions:
C2H6, C3H8, C3H6, C2H2 and CH4.
Answer 13 Unsaturated hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions. Being unsaturated hydrocarbons, C3H6 and C2H2 undergo addition reactions.
Question 14. Give a test that can be used to differentiate between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Answer 14 Butter contains saturated fats. Therefore, it cannot be hydrogenated. On the other hand, oil has unsaturated fats. That is why it can be hydrogenated to saturated fats (solids).
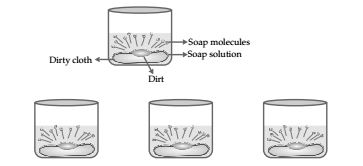
Question 15. Explain the mechanism of the cleaning action of soaps.
Answer 15 Cleaning action of soaps: The dirt (oil and grease) present on clothes is organic in nature, and insoluble in water. Therefore, it cannot be removed only by washing with water. When soap molecules are present in water, the molecules arrange themselves in the form of a cluster in such a manner that their hydrophobic ends are away and away from the water molecules and their hydrophilic or ionic ends are towards the water molecules. When soap is dissolved in water, its hydrophobic ends attach themselves to the dirt and remove it from the cloth.
Then, the molecules of soap arrange themselves in micelle formation and trap the dirt at the centre of the cluster. These micelles remain suspended in water like particles in a colloidal solution. The various micelles present in water do not come together to form a precipitate as each micelle repels the others because of ion-ion repulsion. Thus, the dust particles remain trapped in the micelles (which remain suspended), and are easily washed away by water. Therefore, soap micelles remove the dirt by dissolving it in water as in the given figure.
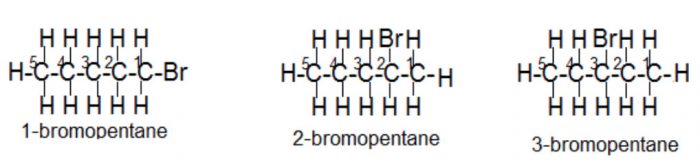
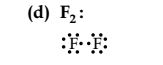
Leave a Reply