Question 1 What is meant by soil profile? Draw a sketch of the soil profile and label the various layers?
Question 2 What is soil? How is soil formed?
Question 3 Define the term humus?
Question 4 State few important uses of soil?
Question 5 What is meant by weathering?
Question 6 Name the various types of rock particles present in soil?
Contents
Soil
The uppermost layer of earth’s crust (in which plants grow) is called soil.
Humus
Soil is a dark brown (or black) solid material which is a mixture of rock particles of various sizes and decayed plant and animal matter called humus. Soil also contains air, water and countless living organisms.
Soil is essential for the existence of life on the earth. Soil supports the growth of plants (and trees) by holding their roots firmly and by supplying them with water and nutrients.
Important uses of Soil
(1) Soil is used for growing food (like grains, pulses, fruits and vegetables, etc.).
(2) Soil is used to grow trees for obtaining wood for building purposes (timber), for burning as fuel (firewood) and for making paper.
(3) Soil is used to grow cotton plants which give us cotton clothes. Soil is also used to grow mulberry trees for rearing silkworms which provide us silk for making silk clothes.
(4) Soil is used to make bricks and mortar for building houses.
(5) Soil is used to make earthenware or pottery (such as matkas, surahis, etc.), crockery (cups and plates), toys and statues, etc.
The process by which huge rocks are broken down into small particles by the action of sun’s heat, wind, rain and flowing river water, etc. is called weathering.
The organic matter formed by the decomposition of dead plants and animals by the micro-organisms (like certain bacteria and fungi) is called humus. Humus contains nutrients (like nitrogen and phosphorus, etc,) which are needed by the plants for their growth.
Formation of Soil
Soil is formed from rocks by the process of weathering. In weathering, rocks are broken down very slowly by the action of sun’s heat, wind, rain, flowing river water, etc. to form tiny rock particles. These tiny rock particles then mix up with humus to form fertile soil. The nature of any soil depends on the rocks from which it has been formed and the type of vegetation that grows in it.
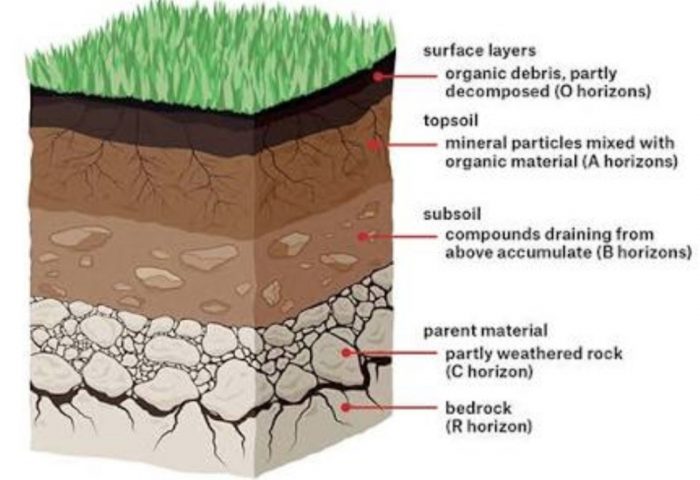
Soil Profile
A vertical section (or cutting) through the soil showing the different layers of soil is called soil profile. Soil profile consists of three different layers of soil.
Horizon
Each layer of soil is called a horizon. The three lavers of soil in the soil profile are:
1) A-horizon (or Top-soil)
2)B-horizon (or Sub-soil)
3)C-horizon (or Sub-stratum)
A-Horizon (or Top-Soil)
The top layer of soil is called A-horizon. Top soil is dark in colour. This is because top-soil is rich in minerals and humus. The plant roots grow in the top-soil. The top-soil contains many living things. Top-soil contains a lot of decayed dead plants and animal remains.
In other words, top-soil contains a lot of humus. This humus makes the top-soil very fertile. The top-soil is soft and porous, and can hold more of water. The top-soil is rich in minerals which the plants need for growth. Top-soil is the most useful part of the soil.
B-Horizon (or Sub-Soil)
The layer of soil which is just below the top-soil is called B-horizon. It is also known as sub-soil. The sub-soil is made up of slightly bigger rock particles than that of top-soil. It is somewhat harder and more compact than the top-soil. Sub-soil is also lighter in colour than the top-soil. The sub-soil contains very little living organisms. The roots of some of the trees are, however, able to reach sub-soil.
The sub-soil has very little humus (decayed organic matter). Due to this, sub-soil is much less fertile as compared to the top-soil. Sub-soil is rich in soluble minerals.
C-Horizon (or Sub-Stratum)
The layer of soil which is just below the sub-soil is called C-horizon. It is also called sub-stratum. Sub-stratum is made up of small lumps of broken rocks (or stones) formed by the partial weathering of bed-rock (or parent rock).
Below the C-horizon we have unweathered solid rock called bed-rock (or parent rock).It is this bed-rock (or parent rock) which has produced the soil over a long period of time.
The soil is made up of six components: Rock particles (of different sizes), Minerals, Humus (Organic matter), Air, Water and Living organisms. The rock particles present in soil are of different sizes and chemical compositions.
On the basis of their sizes, the rock particles present in soil can be divided mainly into four groups: Clay, Silt, Sand and Gravel.
1) The smallest rock particles present in soil form clay. Because of its very small particles, clay feels smooth to touch.
(2) The rock particles in soil which are a little larger than clay particles form silt. Thus, silt is made up of rock particles somewhat bigger than that of clay. Due to its slightly bigger sized particles, silt is not so smooth. Actually, the size of silt particles is in-between that of clay and sand. The size of silt particles is bigger than that of clay particles but smaller than those of sand particles. Silt occurs as a deposit in river beds.
(3) The rock particles in soil which are larger than silt particles form sand. Being quite large, sand particles can be easily seen by us. And because of its large sized particles, sand is coarse to touch.
(4) The largest sized rock particles present in soil are called gravel. Gravel is a kind of tiny stones. The amount of gravel present in a good top-soil is very small.
In a good top-soil, gravel is present in very small amount. The main rock particles present in the top-soil are sand, clay and silt.
So, depending on its composition, a soil can be classified as sandy soil, clayey soil or loamy soil. All these soils have different proportions of rock particles of different sizes. The sizes of rock particles in a soil have a very important influence on the properties of that soil.
This site should be made for all the class’s students like class 9,10,11,12 etc. So that they can prepare their notes easily and don’t find any difficulties in study.
Thank you
Amritesh Raj
This helped me so much
Thank you so much for making this available! I really appreciate the simple, yet precise, way you have covere3d this topic!
Jenny