Chapter 4 Notes
Maps
Class 6 – Social Science
| Class | Class 6 |
| Subject | Social Science |
| Chapter Name | Maps |
| Chapter No. | Chapter 4 |
| Category | Class 6 Geography Notes |
Question 1 What is the limitation of Globe?
Question 2 What is a map? Describe its features.
Question 3 Differentiate between globe and map?
Question 4 What is an atlas?
Question 5 How will you classify maps on the basis of their scale?
Question 6 How will you classify maps on the basis of their function?
Question 7 What are the components of maps?
Question 8 Define the term scale, map distance and ground distance.
Question 9 Name the cardinal and intermediate directions.
Question 10 How can you find direction by facing the Sun?
Question 11 How can you find direction with the magnetic compass?
Question 12 How can the pole star help in finding direction?
Question 13 What is a sketch?
Question 14 What is a plan?
Question 15 What are symbols? Why do we need them?
Question 16 Why do we use colours on map?
Question 17 What is compass and how does it works?
Contents
Limitations of Globe
1) It is difficult to carry a globe.
2) The space on the globe is limited and details cannot be shown on it.
3) Details of the geographic features cannot be shown properly.
4) It is difficult to make and handle a big size globe.
When we want to study only a part of the earth, as about our country, states, districts, towns and villages, the globe is of little help. Then we use maps.
A map is a representation or a drawing of the earth’s surface or a part of it drawn on a flat surface according to a scale.
It is not easy to draw map on a flat surface. Maps are useful to us for various purposes. One map shows a small area and a few facts. Another map may contain as many facts as a big book.
A book of maps is called an atlas. Atlases are of various sizes, measurements drawn on different scales.
Types of Maps
a) Based on the scale of the map
1) Large scale map
2) Small scale map
1) Large-scale map – They show a very small area in detail. The layout of villages and the guide maps of cities are large-scale maps.
2) Small-scale maps – They show a very large area with fewer details. The maps in an atlas or wall maps used in classrooms are small-scale maps.
b) Based on the function of the map
1) Physical maps
2) Political maps
3) Thematic maps
1) Physical maps – Maps showing relief features of the earth such as mountains, plateaus, plains, rivers, oceans etc. are called physical or relief maps. These maps help us to find suitable sites for human settlement, for building roads and railways, for construction of dams etc.
2) Political maps – Those maps which show cities, towns villages, and different countries and states of the world with their boundaries are called political maps. These maps are used as base maps for showing various cultural, historical and economic activities.
3) Thematic maps – Some maps focus on specific information; such as roads, rainfall, distribution of forests, condition of climatic elements, location of mining, industries etc. are known as thematic maps.
Components of Maps
There are three components of Maps – distance, direction and symbol.
1) Distance – It means the space between any two places.It can be short or long.It is related to the time taken to reach a destination.
Maps are drawings, which reduce the entire world or a part of it to fit on a sheet of paper. Or we can say maps are drawn to reduced scales. But this reduction is done very carefully so that the distance between the places is real.
It can only be possible when a small distance on paper represents a large distance on the ground. Therefore, a scale is chosen for this purpose.
Scale is the ratio between the map distance and the ground distance.
Map Distance – The distance between any two places on a map is measured along is called the map distance.
Ground Distance – The distance between the same two points on the ground measured along a straight line is called the ground distance.
For example, The distance between your school and your home is 10 km. If you show this 10 km. distance by 2 cm on a map, it means, 1 cm on the map will show 5 km. on the ground.
The scale of your drawing will be 1cm = 5 km.
Thus, scale is very important in any map.
If you know the scale, you will be able to calculate the distance between any two places on a map.
When large areas like continents or countries are to be shown on a paper, then we use a small scale. For example, 5 cm. on the map shows 500 km. of the ground. It is called a small-scale map.
When a small area like your village or town is to be shown on paper, then we use a large scale that is 5 cm. on the map shows 500 metres only on the ground. It is called a large scale map.
Large-scale maps give more information than small-scale maps.
2) Direction – Most maps contain an arrow marked with the letter ‘N’ at the upper right hand corner. This arrow shows the north direction. It is called the North Line. When you know the north, you can find out other directions, for example east, west and south.
There are four major directions, North, South, East and West . They are called cardinal directions.
Other four intermediate directions are north-east (NE), southeast(SE), south-west (SW) and north-west (NW). We can locate any place more accurately with the help of these intermediate directions.
Finding Direction
1) By facing the rising Sun – the Sun rises in the east and sets in the west. If we stand facing the sun in the morning, we face the east. The west is towards our back. The left hand points towards the north and the right hand points towards the south.
2) With the help of a magnetic compass – It is used to find the direction. The needle of the magnetic compass is always towards the north-south direction.
3) By Pole Star – The pole star is located vertically above the North Pole. In the Northern hemisphere the constellation known as Great Bear keeps revolving around the pole star. The two-pointer stars of the Great Bear always point towards the Pole star.
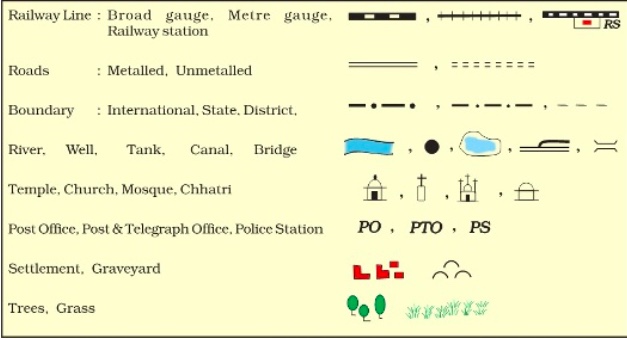
3) Symbols – It is not possible to draw on a map the actual shape and size of different features such as buildings, roads, bridges, trees, railway lines or a well.
So, they are shown by using certain letters, shades, colours, pictures and lines. These symbols give a lot of information in a limited space.
With the use of these symbols, maps can be drawn easily and are simple to read.
Maps have a universal language that can be understood by all. There is an international agreement regarding the use of these symbols. These are called conventional symbols.
Various colours are used for the same purpose. For example, generally blue is used for showing water bodies, brown for mountain, yellow for plateau and green for plains.
Sketch
A sketch is a drawing which is drawn without measuring the distance between various places.
Sometimes a rough drawing is required of an area to tell where a particular place is located with respect to other places.
Suppose, you want to go to your friend’s house, but you don’t know the way. Your friend may make a rough drawing to show the way to his house. Such a rough drawing is drawn without scale and is called a sketch map.
Plan
A plan is a drawing of a small area on a large scale. The scale of a plan is different from that of a map. For example: 1 cm on a plan may represent 1m on the ground.
A large-scale map gives lot of information and is drawn on a small scale. For example: 1 cm on a map represents 100 Km on the ground.
Leave a Reply