Question 1 What is Dobereiner’s triad? Give few examples?
Question 2 What were the limitations of Dobereiner’s classification of elements?
Question 3 What is Newland’s law of Octaves? Give an example
Question 4 What were the limitations of Newland’s law of Octaves?
Contents
Dobereiner’s Triads
Johann Dobereiner, a German chemist, arranged certain elements with similar properties (both physical and chemical) in groups of three called triads.
The basis of the arrangement was the atomic masses of the elements. In a particular triad, the element(A,B,C) were arranged in order of increasing atomic masses and the atomic mass of the middle element was almost the mean or the average of the atomic masses of the first and third elements i.e. A and C.
Atomic mass of the element (B) = ½ [Atomic mass of the element (A) + Atomic mass of the element (C)]
These triads are popularly known as Dobereiner’s triads.
Triad of Li, Na and K
These elements are known as Alkali metals and are arranged in order of increasing atomic masses.
| Element | Lithium | Sodium | Potassium |
| Atomic mass(u) | 6.9 | 23 | 39 |
Some common properties of the elements present in the triad are:
(1) All the elements are metals
(2) All of them react with water to form soluble hydroxides known as alkalies and evolve hydrogen gas.
For example: 2Na + 2H2O ——–> 2NaOH + H2
(3) All of them are monovalent which means that they exhibit valency of one in their compounds.
Triad of Ca, Sr, Ba
The elements are also present in the same triad and known as alkaline earth metals.
| Element | Calcium | Strontium | Barium |
| Atomic mass (u) | 40.1 | 87.6 | 137.3 |
The elements have a few common characteristics.
(1) All these elements are metals.
(2) All of them show valency of two in their compounds.
(3) All of them impart characteristic colours to the flame.
Triad of Cl, Br and I
The first two triads are of metals. But the elements included in this triad are non-metals. These are known as halogens.
| Element | Chlorine | Bromine | Iodine |
| Atomic mass | 35.5 | 79.9 | 126.9 |
A few common characteristics of the members of the halogen family are :
(1) All the elements are non-metals and diatomic gases (Cl2, Br2, I2)
(2) All of them react with water to form acids known as halogen.
(3) All the members of the family show valency of one in their compounds.
(4) All of them are highly reactive chemically.
Limitations of Dobereiner’s Triads
He could not arrange all the elements known at that time into triads. He could identify only three such triads that have been mentioned.
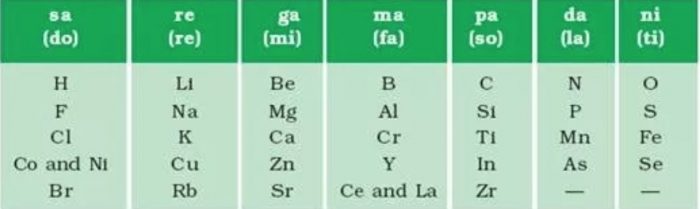
Newland’s Law Of Octaves
John Newlands , an English scientist in 1866 arranged about 56 elements known at that time in order of increasing atomic masses.
According to Newlands’ Law of Octaves
When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic masses, there is a repetition of the properties of every eighth element as compared to the given element.
These are seven musical notes according to Indian system, these musical notes are sa, re, ga, ma, pa da, ni. According to Western system, the corresponding symbols of these notes are do, re, me, fa, so, la ti. In the musical notes, there is a repetition of the same note after a gap of seven. By coincidence, Newland found the same pattern in the arrangement of the elements.
These elements placed in the same vertical row also known as group, have common properties. The elements Be, Mg and Ca are grouped on similar basis and they resemble in their characteristics.
Limitations of Newlands Law of Octaves
1) Classification was successful only up to the element calcium. After that, every eighth element did not possess the same properties as by the element lying above it in the same group.
For example: The elements Co and Ni placed below chlorine had different properties.
2) He placed two elements in the same slot in a particular group.
For example: Co and Ni in the first group after chlorine. Similarly. elements cerium (Ce) and lanthanum (La) were placed after yitterium (Y) in the same group. Newland could not offer any explanation for such an arrangement.
3)Newland somehow thought that only 56 elements existed in nature and no more elements were likely to be discovered. But this belief ultimately proved to be wrong.
4) When noble gas elements were discovered at a later stage, their inclusion in the table disturbed the entire arrangement.
Leave a Reply