Question 1 What are voluntary actions?
Question 2 What are involuntary actions?
Question 3 What is cranium? What is its function?
Question 4 What are meninges. What is their function?
Question 5 Name the three regions of brain?
Question 6 What are the functions of fore brain?
Question 7 What are the functions of mid brain?
Question 8 What are the functions of hind brain?
Question 9 What are the two parts of central nervous system?
Question 10 Explain the function of spinal cord?
Contents
Central Nervous System
a) Brain
b) Spinal cord
Brain
It is the highest coordinating centre in the body.
It is situated in cranial cavity of skull called cranium. It protects the brain from mechanical shock.
It is contained in a fluid filled balloon which provides further shock absorption.
It consist of 100 billion nerve cell.
It is surrounded by 3 membranes called meninges which provide protection to it.
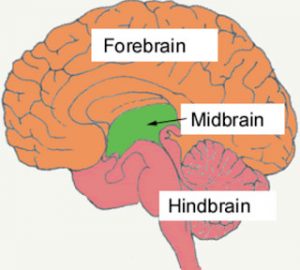
Brain has 3 parts :
1) Fore brain
2) Mid brain
3) Hind brain
Forebrain
It forms the greater part of the brain.
It has 3 regions which receive sensory impulses from receptors.
There are separate areas which specialised for hearing, smell, sight etc.
There are areas of association where this sensory information is interpreted by putting it together with information that is already stored in brain.
Based on all these a decision is made how to respond and information is passed on to motor area which control movement of voluntary muscles.
Mid Brain
(1) It controls reflex movement of head, neck, trunk in response to visual and auditory part.
(2) It controls eye muscles, change in pupil size.
Hind Brain
(1) It controls balance of body ie posture, respiration, rate of heart beat, respiration, rate of heart beat, expansion and contraction of blood vessels, swallowing, coughing, sneezing.
It has 3 parts:
(1) Cerebellum
(2) Pons
(3) Medulla
Spinal Cord
It has cylindrical structure,45 cm long, it begins in continuation with medulla and extends downwards.
It is enclosed in backbone.
31 pairs of spinal nerves arises from spinal cord.
Function of Spinal Cord
1) It conduct sensory and motor impulse to and from the brain.
2) It act as a centre for reflex actions.
Involuntary Action
They are performed without will of organism.
For Example : Blood pressure, heart beat, movement of diaphragm, salivation, vomiting etc.
Voluntary action
They are performed by organism with its will.
easy to understand