Question 1 Explain the covalent bonding in Methane.
Question 2 Explain the covalent bonding in Ethane.
Question 3 What are saturated compounds?
Question 4 What are unsaturated compounds?
Question 5 Explain the covalent bonding in Ethene.
Question 6 Explain the covalent bonding in Ethyne.
| Class | Class 10 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter Name | Carbon and its Compound |
| Chapter No. | Chapter 4 |
| Topic | Saturated and Unsaturated Compounds |
| Category | Class 10 Science Notes |
Contents
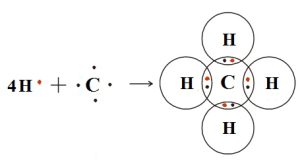
Structure of Methane
Methane is a tetrahedral molecule with four equivalent C-H bonds. It consists of four hydrogen atoms and one carbon atom. Its formula is CH4. The covalent bond is formed by the sharing of electrons between the atoms to form the compound. In methane, the four electrons of carbon bind with the four electrons of four hydrogen atoms to form four covalent bonds. In methane, carbon atoms are bonded with four hydrogen atoms.
Structure of Ethane
Ethane is a molecule with molecular formula C2H6.It contains two carbons and 6 hydrogens. In ethane three valencies of each carbon atom remain unsatisfied, so each is bonded to three hydrogen atoms.
Saturated compounds
They are hydrocarbons in which only single bonds are present between all Carbon atoms. Saturated hydrocarbons are known alkanes. These compounds are normally not very reactive.
For example Methane, ethane, propane, butane, etc.
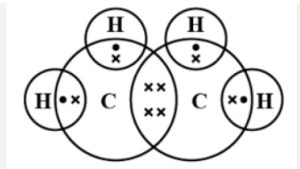
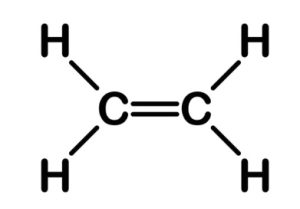
Structure of Ethene
The molecular formula of Ethene is C2H4. Ethene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon having a double bond between two carbon atoms and single bond between four hydrogen atoms.
Each carbon has 4 valence electrons, from which it will use 2 of the electrons from each carbon to make a double bond between them and the rest of the 2 electrons from each carbon will be used to make a total of 4 single bonds with 4 hydrogen single atoms.
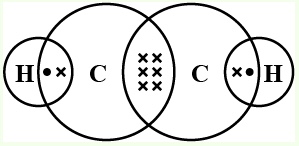
Structure of Ethyne
The molecular formula of Ethyne is C2H2. Ethyne (or acetylene) is an unsaturated hydrocarbon since it contains a carbon-carbon triple bond each of which is singly bonded to one other hydrogen atom.
Each carbon has 4 valence electrons, from which it will use 3 of the electrons from each carbon to make a triple bond between them and the rest of the 1 electrons from each carbon will be used to make a total of 2 single bonds with 2 hydrogen single atoms.
Unsaturated Compounds
They are hydrocarbons that contain double and triple covalent bonds between two carbon atoms. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are known as alkenes and alkynes.
For example: Ethene, propene, butene, etc.
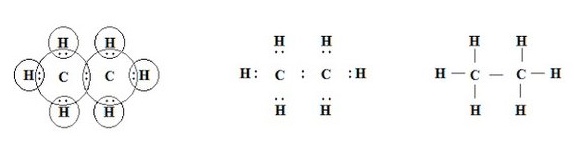
Leave a Reply