Question 1 Name the two allotropes of Carbon.
Question 2 Explain the structure of a Diamond.
Question 3 Explain the structure of Graphite.
Question 4 Write a few properties of Diamond.
Question 5 Write a few properties of Graphite.
Question 6 What are Fullerenes?
Question 7 Differentiate between Diamond and Graphite?
| Class | Class 10 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter Name | Carbon and its Compound |
| Chapter No. | Chapter 4 |
| Topic | Allotropes of Carbon |
| Category | Class 10 Science Notes |
Diamond and Graphite are two allotropes of carbon i.e. pure forms of the same element that differ in structure.
Both diamond and graphite are formed by carbon atoms, the difference lies in the manner in which the carbon atoms are bonded to one another.
These two different structures result in diamond and graphite having very different physical properties even though their chemical properties are the same.
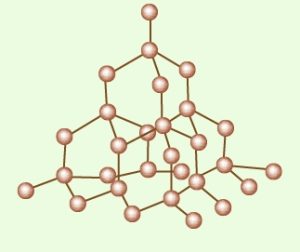
Diamond
It has a number of carbons linked together tetrahedrally. Each tetrahedral unit consists of carbon bonded to four carbon atoms which are in turn bonded to other carbons. This gives rise to an allotrope of carbon having a three-dimensional arrangement of C-atoms.
It is hard because breaking a diamond crystal involves rupturing many strong covalent bonds.
Properties of Diamond
1) Diamond is the hardest known substance.
2) It has a very high melting point.
3) Diamonds can be synthesised by subjecting pure carbon to very high pressure and temperature.
4) It has a high relative density and refractive index.
5) It is a bad conductor of electricity
6) It is a good conductor of heat
7) It is insoluble in all solvents
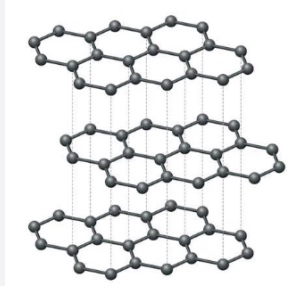
Graphite
In graphite, each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms in the same plane giving a hexagonal array. One of these bonds is a double-bond, and thus the valency of carbon is satisfied. Graphite structure is formed by the hexagonal arrays being placed in layers one above the other.
Properties of Graphite
1) Graphite is smooth and slippery.
2) Graphite is used as a dry lubricant for machines at high temperatures.
3) Since the layers are stacked over each other, this carbon allotrope can act as a lubricant.
4) It also has a metallic lustre, which helps in the conduction of electricity. It is a very good conductor of both heat and electricity.
Fullerenes form another class of carbon allotropes. The first one to be identified was C-60 which has carbon atoms arranged in the shape of a football. Since this looked like the geodesic dome designed by the US architect Buckminster Fuller, the molecule was named fullerene.
Leave a Reply