Class 9 Science Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms NCERT Solutions Page 80 1. Why do we classify organisms? Answer: There are millions of organism or species on earth. It is very difficult to study all of them one by one. The method of arranging organism into groups or sets on the basis of similarities and differences is called classification. Classification … [Read more...] about Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms
Class 9
Chapter 6 Tissues
Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues NCERT Solutions Page 69 1. What is a tissue? Answer: Tissue is a group of cells that are similar in structure and are organised together to perform a specific task. 2. What is the utility of tissues in multi-cellular organisms? Answer: In multicellular organisms, cells are grouped to form tissues. These tissues are specialised to … [Read more...] about Chapter 6 Tissues
Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
Class 9 Science Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life NCERT Solutions Page 59 1. Who discovered cells, and how? Answer: Cells were discovered in 1665 by an English Botanist, Robert Hooke. He used a primitive microscope to observe cells in a cork slice. 2. Why is the cell called the structural and functional unit of ? Answer: Cell is the smallest unit of life … [Read more...] about Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
Chapter 4 Structure of the Atom
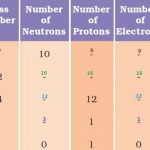
Class 9 Science Chapter 4 Structure of the Atom NCERT Solutions Page 47 1. What are canal rays? Answer: Canal rays are positively charged radiations. These rays consist of positively charged particles known as protons. They were discovered by Gold stein in 1886. 2. If an atom contains one electron and one proton, will it carry any charge or not? Answer: Since an … [Read more...] about Chapter 4 Structure of the Atom
Chapter 3 Atoms and Molcules
Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules NCERT Solutions Page 32, 33 1. In a reaction, 5.3 g of sodium carbonate reacted with 6 g of acetic acid. The products were 2.2 g of carbon dioxide, 0.9 g water and 8.2 g of sodium acetate. Show that these observations are in agreement with the law of conservation of mass. sodium carbonate + acetic acid → sodium acetate + carbon … [Read more...] about Chapter 3 Atoms and Molcules