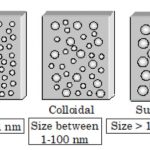
Colloidal State Certain solutes such as starch, glue, gelatin etc. could not pass through the parchment membrane while the ordinary solutes such as sodium chloride, urea , sugar etc. can easily do so. Thus, colloid is not a substance but it is a state of a substance which depends upon the molecular size. Three Types of Solutions On the basis of particle size of the … [Read more...] about Colloidal State
Surface Chemistry
Mechanism of Enzyme Catalysed Reaction and Zeolites
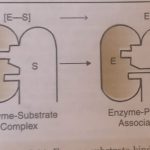
Mechanism of Enzyme Catalysed Reactions The various steps involved in the enzyme catalysed reaction are given below: Step 1. Binding of the enzyme (E) to substrate (S) to form enzyme-substrate complex. E + S ⇔ ES (fast, reversible) ES is called the enzyme-substrate complex. Step 2. Dissociation of enzyme-substrate complex to form the products. ES -------> EP … [Read more...] about Mechanism of Enzyme Catalysed Reaction and Zeolites
Enzyme Catalysis
Enzymes Large number of organic reactions are taking place in the body of animals and plants to maintain the life processes. These reactions are catalysed by complex nitrogenous organic compounds known as enzymes. These are also called biological catalysts or biochemical catalysts and are produced by the living cells in plants and animals. Thus, enzymes are biological … [Read more...] about Enzyme Catalysis
Mechanism of Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Catalyst
Mechanism of Homogeneous Catalytic Reactions The catalyst combines with one of the reactants to form an intermediate. Intermediate compound being unstable either decomposes or combines with the other reactant form the product and the catalyst is regenerated. For Example: the combination of SO2 and O2 to form SO3 is a slow process. However, in the presence of NO (catalyst) … [Read more...] about Mechanism of Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Catalyst
Modern Adsorption Theory and Features of Solid Catalyst
Adsorption Theory The surface of the catalyst has free valencies which provide sites for chemical forces of attraction. The reactants in the gaseous state or in solution are adsorbed on the surface of the solid catalyst. As the reactant molecules are adsorbed, its bonds are weakened and the reaction can proceed quickly because the bonds are more quickly broken. For … [Read more...] about Modern Adsorption Theory and Features of Solid Catalyst