Class 8 Science Chapter 9 |
Reproduction in Animals NCERT Solutions
1. Explain the importance of reproduction in organisms.
The production of new organism from the existing organism of the same species is known as reproduction. Reproduction is the creation of new living things. It is essential for the survival of species on this earth. So, living organism produce more organism of their kind to maintain the life of their species on this earth. Reproduction gives rise to more organism with the same basic characteristics as their parents.
2. Describe the process of fertilisation in human beings.
The fusion of male gamete(sperm) with female gamete(egg)give rise to a new cell called zygote. The fusion of male gamete with a female gamete to form a zygote during sexual reproduction is called fertilisation.
3. Choose the most appropriate answer.
(a) Internal fertilisation occurs
(i) in female body.
(ii) outside female body.
(iii) in male body.
(iv) outside male body.
Answer:
(i) in female body.
(b) A tadpole develops into an adult frog by the process of
(i) fertilisation (ii) metamorphosis (iii) embedding (iv) budding
Answer:
(ii) metamorphosis
(c) The number of nuclei present in a zygote is
(i) none (ii) one (iii) two (iv) four
Answer:
(ii) one
4. Indicate whether the following statements are True (T) or False (F).
(a) Oviparous animals give birth to young ones. ( )
(b) Each sperm is a single cell. ( )
(c) External fertilisation takes place in frog. ( )
(d) A new human individual develops from a cell called gamete. ( )
(e) Egg laid after fertilisation is made up of a single cell. ( )
(f) Amoeba reproduces by budding. ( )
(g) Fertilisation is necessary even in asexual reproduction. ( )
(h) Binary fission is a method of asexual reproduction. ( )
(i) A zygote is formed as a result of fertilisation. ( )
Answer:
(a) Oviparous animals give birth to young ones. (F)
(b) Each sperm is a single cell. (T)
(c) External fertilisation takes place in frog. (T)
(d) A new human individual develops from a cell called gamete. (F)
(e) Egg laid after fertilisation is made up of a single cell. (T)
(f) Amoeba reproduces by budding. (F)
(g) Fertilisation is necessary even in asexual reproduction. (F)
(h) Binary fission is a method of asexual reproduction. (T)
(i) A zygote is formed as a result of fertilisation. (T)
(j) An embryo is made up of a single cell. (F )
5. Give two differences between a zygote and a foetus.
| Zygote | Foetus |
| The fusion of male gamete(sperm) with female gamete(egg)give rise to a new cell called zygote | An unborn baby in the uterus at the stage when all the body parts can be identified is called foetus. |
| Zygote is single cellular | Foetus is multicellular. |
6. Define asexual reproduction. Describe two methods of asexual reproduction in animals.
Asexual reproduction is the production of a new organism from a single parent without the involvement of sex cells or gametes.
The 2 common methods of asexual reproduction are:
1)Binary Fission
In binary fission the parent organism splits or divides to form two new organism.
The unicellular organism called amoeba reproduces by the method of binary fission. Amoeba reproduces by binary fission by dividing its body into 2 parts. When the amoeba cell reached its maximum size of growth, then first nucleus of amoeba lengthens and divides into two parts. After that the cytoplasm of Amoeba divides into 2 parts, one part around each nucleus. One parent amoeba divides to form two smaller amoebae(Daughter amoebae).One amoeba produces two amoebae. It takes about an hour to divide into 2 daughter amoebae. The two daughter amoebae produced here grow to their full size by eating food and then divide again to produce four amoebae, and so on. The daughter amoebae produced by the process are identical to the parent amoeba.
2)Budding
Bud means a small outgrowth from the body of an organism. When a bud is formed on the body of an organism, then the nucleus divides into two and one of the nuclei passes into the bud.
In budding, a small part of the body of the parent organism grows out as a bud which then detaches and becomes a new organism.
For Example : Hydra, sea-anemones, sponges and corals reproduce by the method of budding.
In hydra, first a small outgrowth called bud is formed on the side of its body by the repeated divisions of its cells. This bud then grows gradually to form a small hydra by developing a mouth and tentacles. And finally the tiny new hydra detaches itself from the body of parent hydra and lives as a separate organism. The parent hydra has produced a new hydra. The bud formed in a hydra is not a single cell. It is a group of cells.
7. In which female reproductive organ does the embryo get embedded?
Embryo gets embedded in walls of uterus in female reproductive organ.
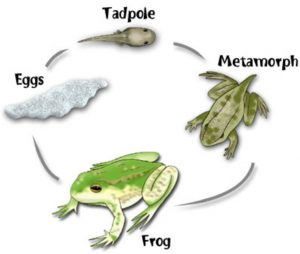
8. What is metamorphosis? Give examples.
The transformation of larvae into an adult through drastic changes in appearance is called metamorphosis. The change of a larvae to an adult animal is metamorphosis. It occurs in amphibians and insects(silk moth, butterfly, housefly).The hatching of a fertilised egg of frog produces a very immature young one called tadpole. The tadpole or larvae of frog develops gradually and undergoes many drastic changes in appearance before it forms an adult frog. The tadpole looks very different from adult frog.
9. Differentiate between internal fertilisation and external fertilisation.
| Internal fertilisation | External fertilisation |
| 1) The fertilisation which take place inside the female body is called internal fertilisation. | The fertilisation which take place outside the female body is called external fertilisation. |
| 2) Less number of eggs are produced. | Large number of eggs are produced |
| 3) For Ex: human, cow, dogs etc | For Ex: fish, frog |
10. Complete the crossword puzzle using the hints given below.
Across
1. The process of the fusion of the gametes.
6. The type of fertilisation in hen.
7. The term used for bulges observed on the sides of the body of hydra.
8. Eggs are produced here.
Down
2. Sperms are produced in these male reproductive organs.
3. Another term for in vitro fertilisation.
4. These animals lay eggs.
5. A type of fission in amoeba.
Answer:
Across
1) Fertilization
6) Internal
7) Buds
8) Ovary
Down
2) Testis
3) Zygote
4) Oviparous
5) Binary

Nice app