Page 128
Question 1. What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction?
Answer 1 DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material found in the chromosomes, which are present in the nucleus of a cell. Additional copies of DNA are made during replication which is necessary for the new cells formed after cell division. Copying of DNA is the basic event of reproduction because DNA present in the cells undergoing reproduction produces its copy so that the information for the development of characters may pass over to the next generation through dividing cells or gametes.
Question 2. Why is variation beneficial to the species but not necessarily for the individual?
Answer 2 A species encompasses a large number of individuals. Each individual may have specific type of variations of different nature. These variations are beneficial to the species than individual because sometimes for a species, the environmental conditions change so radically that their survival becomes difficult.
For example: If the temperature of water increases suddenly, then most of the bacteria living in that water would die. Only few variants that are resistant to heat would be able to survive. However, if these variants were not there then the entire species of bacteria would have been destroyed.
Page 133
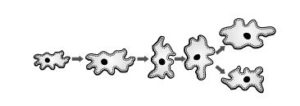
Question 1. How does binary fission differ from multiple fission?
Answer 1
| Binary Fission | Multiple Fission |
| A single cell divides into two equal halves, that is, two daughter cells are formed. | A single cell divides into many daughter cells at once, that is, multiple daughter cells are formed. |
| Happens during favourable conditions. | Happens during unfavourable conditions. |
| It is a routine process. | It is utilised to tide over unfavourable conditions. |
| Example: Amoeba and Bacteria. | Example: Amoeba and Plasmodium |
 |
 |
Question 2. How will an organism be benefited if it reproduces through spores?
Answer 2 There are many advantages, if an organism reproduces through spores.
Advantages of spore formation are:
(i) Large numbers of spores are produced in one sporangium.
(ii) Spores are distributed easily by air to far-off places to avoid competition at one place. Thus, spores can be spread through water, air or animals and thus is good for the spread of an organism to more places.
(iii) Spores are covered by thick walls to prevent dehydration under unfavourable conditions and can remain dormant till favourable conditions become available.
Question 3. Can you think of reasons why more complex organisms cannot give rise to new individuals through regeneration?
Answer 3 Regeneration happens through mitosis and the process involves the formation of new organisms from its body parts. In complex organisms, different tissues and organs have altogether different structures. All the organ systems of their body work together as an interconnected unit. They can regenerate their lost body parts such as skin, muscles, blood, etc.
(i) Regenerating a different kind of tissue from another kind is not possible. Therefore, complex organisms are unable to give rise to new individuals through regeneration.
(ii) But, simple organisms such as Hydra and Planaria are capable of producing new individuals through the process of regeneration.
(iii) Simple organisms can utilize this method of reproduction as their entire body is made of similar kind of cells in which any part of their body can be formed by growth and development.
Question 4. Why is vegetative propagation practised for growing some types of plants?
Answer 4 Vegetative propagation practiced for growing some types of plants because it takes less time to grow a plant and different traits of a species can be developed on the same plant through this process. Many plants grown through vegetative propagation take less time to give fruits and other beneficial plant produce.
Question 5. Why is DNA copying an essential part of the process of reproduction?
Answer 5 DNAs are the carriers of genetic information. For an organism to produce its own kind, it becomes necessary that the offspring get similar DNAs as in parents. DNA replication is the way through which a cell makes additional copies of DNA so that they can be transferred to the offspring.
Page 140
Question 1. How is the process of pollination different from fertilisation?
Answer 1 Pollination is the process of transfer of pollens from anther to stigma. It occurs with the help of definite pollinators such as air, water, birds, or some insects. Whereas, fertilization is the fusion of the male and female gametes. It occurs inside the ovule and leads to the formation of zygote.
Question 2. What is the role of the seminal vesicles and the prostate gland?
Answer 2 The secretions from seminal vesicles and prostate glands lubricate the sperms and offer a fluid medium for easy transport of sperms. Their secretion also provides nutrient in the form of fructose, calcium, and some enzymes.
Question 3. What are the changes seen in girls at the time of puberty?
Answer 3 (i) Increase in breast size and darkening of skin of the nipples present at the tips of the breasts.
(ii) Appearance of hair in the genital area.
(iii) Appearance of hair in other areas of skin like underarms, face, hands, and legs.
(iv) Increase in the size of uterus and ovary.
(v) Start of menstrual cycle.
(vi) More secretion of oil from the skin, which results in the appearance of pimples.
Question 4. How does the embryo get nourishment inside the mother’s body?
Answer 4 The embryo develops inside the mother’s body for about nine months. Inside the uterus, the outer tissue surrounding the embryo develops finger-like projections called villi. These villi are surrounded by uterine tissue and maternal blood. They provide a large surface area for exchange of oxygen and nutrients. Also, there is a special tissue called placenta, which is embedded in the uterine wall. The embryo receives the oxygen and nutrients from the mother’s blood via the placenta.
Question 5. If a woman is using a copper-T, will it help in protecting her from sexually transmitted diseases?
Answer 5 Using a copper-T will not provide a protection from sexually transmitted diseases, as it only prevents the implantation of the embryo in the uterus and does not prevent the entry of semen.
Page 141
Question 1. Asexual reproduction takes place through budding in
(a) amoeba.
(b) yeast.
(c) plasmodium.
(d) leishmania.
Answer 1: (b)yeast
Asexual reproduction takes place through budding in yeast.
Question 2. Which of the following is not a part of the female reproductive system in human beings?
(a) Ovary
(b) Uterus
(c) Vas deferens
(d) Fallopian tube
Answer 2: (c) Vas deferens
Vas deferens is not a part of the female reproductive system in human beings.
Question 3. The anther contains
(a) sepals.
(b) ovules.
(c) pistil.
(d) pollen grains.
Answer 3: (d) pollen grains
The anther contains pollen grains.
Question 4. What are the advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction?
Answer 4 Advantages of sexual reproduction:
(i) In sexual reproduction, more variations are produced. Thus, it ensures survival of species in a population.
(ii) The new formed individual has characteristics of both the parents.
(iii) Variations are more viable in sexual mode than in asexual one. This is because in a sexual reproduction, DNA has to function inside the inherited cellular apparatus.
Question 5. What are the functions performed by the testis in human beings?
The testes are the male reproductive organs that are located outside the abdominal cavity within a pouch called scrotum.
Functions of testes:
(i) Production of sperms.
(ii) Production of the hormone testosterone.
Question 6. Why does menstruation occur?
Answer 6 Menstruation is a process in which blood and mucous flows out every month through the vagina. This process occurs every month because one egg is released from the ovary every month and at the same time, the uterus (womb) prepares itself to receive the fertilized egg. Thus, the inner lining of the uterus gets thickened and is supplied with blood to nourish the embryo. If the egg does not get fertilised, then the lining of the uterus breaks down slowly in fragments along with the unfertilized egg and gets released in the form of blood and mucous from the vagina.
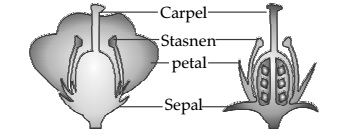
Question 7. Draw a labelled diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower.
Answer 7
Question 8. What are the different methods of contraception?
Answer 8 The contraceptive methods can be broadly divided into the following types:
(i) Natural method: It involves avoiding the chances of meeting of sperms and ovum. In this method, the sexual act is avoided from day 10th to 17th of the menstrual cycle because during this period, ovulation is expected and therefore, the chances of fertilization are very high.
(ii) Barrier method: In this method, the fertilization of ovum and sperm is prevented with the help of barriers. Barriers are available for both males and females. Condoms are barriers made of thin rubber that are used to cover penis in males and vagina in females.
(iii) Oral contraceptives: In this method, tablets or drugs are taken orally. These contain small doses of hormones that prevent the release of eggs and thus fertilization cannot occur.
(iv) Implants and surgical methods: Contraceptive devices such as the loop or Copper-T are placed in uterus to prevent pregnancy. Some surgical methods also can be used to block the gamete transfer. It includes the blocking of vas deferens to prevent the transfer of sperms known as vasectomy. Similarly, fallopian tubes of the female can be blocked so that the egg will not reach the uterus known as tubectomy.
Question 9. How are the modes for reproduction different in unicellular and multicellular organisms?
Answer 9 In unicellular organisms, reproduction occurs by the division of the entire cell or by asexual methods. The modes of reproduction in unicellular organisms can be binary fission, budding, etc. however in multicellular organisms, specialised reproductive organs are present, they use both asexual and sexual methods for reproduction. Therefore, they can reproduce by complex reproductive methods such as vegetative propagation, spore formation, etc. In more complex multicellular organisms such as human beings and plants, the mode of reproduction is sexual reproduction. While simple organisms usually follow the asexual methods of reproduction.
Question 10. How does reproduction help in providing stability to populations of species?
Answer 10 (i) All the living organisms need energy for their survival and growth. This energy is obtained from various life processes such as nutrition and respiration. Thus, these phenomenon are essential for the living of an individual.
(ii) Compared to these life processes, reproduction may appear to be a waste of energy as it is not essential for survival of an individual. But it is an important function of a living being as it help’s in production of new individuals of its own kind.
(iii) Continuity of life has been possible through reproduction Genetic material is transferred from one generation to the next by DNA copying as a result of reproduction.
(iv) DNA copying takes place with high constancy and considerable variations. This is advantageous for maintaining features that allow the organism to survive in the changing environment.
(v) Therefore, reproduction is related to the stability of a species and is not essential for the survival of an individual.
Question 11. What could be the reasons for adopting contraceptive methods?
Answer 11 Contraceptive methods are mainly adopted because of the following reasons:
(i) To prevent unwanted pregnancies.
(ii) To control population, rise or birth rate.
(iii) To prevent the transfer of sexually transmitted diseases.

Really very useful thank you so much..keep doing the same..thank you..
Very nice and useful. Thanks for spreading knowledge