Question 1 What is a rectilinear motion? Give few examples?
Question 2 What is a circular motion? Give example?
Question 3 What is a rotational motion? Give example?
Question 4 What is a periodic motion? Give example?
Question 5 What is the formula to calculate the speed of an object?
Question 6 What is meant by uniform motion? Give example?
Question 7 What is meant by non-uniform motion? Give example?
Question 8 What are the standard units of speed?
Question 9 Name the unit which is used to express large speed?
Question 10 What is speedometer?
Question 11 What is odometer?
Contents
Motion
The movement of an object is called motion. The moment (or duration) in which things occur is called time. An object is said to be in motion (or moving) when its position changes with time.
Different objects show different types of motion (or movements).There are four important types of motion : Rectilinear motion, Circular motion, Rotational motion, and Periodic motion.
Rectilinear Motion
Motion in a straight line is called rectilinear motion. In other words, when an object moves along a straight line path, it is called rectilinear motion.
(1) The motion of a bullock cart moving on a straight road is rectilinear motion.
(2) Motion of a horse pulling a cart on a straight road
(3) Motion of a train on a straight bridge and
(4) March past of soldiers in a parade.
Circular Motion
A round path having the shape of a circle is called circular path. When an object moves along a circular path, it is called circular motion.
(1) The earth moves around the sun in a circular path (or circular orbit), so the motion of the earth around the sun is circular motion.
(2) Motion of a child in a merry-go-round, and
(3) Motion of pedals of a moving bicycle.
Rotational Motion
When an object turns (or spins) about a fixed axis, it is called rotational motion.
(1) The spinning of earth on its axis.
(2) The turning of the blades of a fan
Periodic Motion
The motion which repeats itself after regular intervals of time, is called periodic motion. Periodic motion is also called oscillatory motion.
(1) The swinging of a pendulum
(2) Motion of a swing
(3) Motion of hands of an athlete while running a race
(4) Motion of a child on a see-saw
(5) Motion of hammer in an electric bell
Slow and Fast moving Objects
An object which takes a longer time to cover a certain distance is called slow whereas another object which takes a shorter time to cover the same distance is said to be fast.
The way to find out which of the two objects is moving faster is to compare the distances moved by them in a unit time.
The distance moved by an object in a unit time is called speed of the object. A slow moving object is said to have a low speed. A fast moving object is said to have high speed. A higher speed indicates that a given distance has been covered in a shorter time.
Speed
Speed of an object is the distance travelled by it in unit time.
The speed of an object can be calculated by dividing the distance travelled by the object, by the time taken to travel this distance.
Suppose a car travels a distance of 100 kilometres in 4 hours.Then the speed of this car is given by
Speed = 100 kilometres/ 4 hours
Speed = 25 kilometres per hour
Thus, the speed of this car will be 25 kilometres per hour.
The Distance travelled divided by ‘Time taken’ actually gives us ‘Average speed’ of the car during that time. While travelling in a car or a bus we have noticed that it is very difficult to keep the speed of the car at a constant (or uniform) value because at many places the brakes are to be applied to slow down or stop the car due to various reasons. Thus, the speed of an object is usually not constant and the distance travelled divided by time gives us the average speed during that time.
Units of Speed
The unit of speed depends upon the unit of distance and the unit of time used.
(1) The standard unit of distance is metre’ and the standard unit of time is ‘second: So, the standard unit of speed is metres per second (metres /second). This unit of metres per second is written in short form as m/s. The basic unit of speed is metres per second (m/s)
(2) Another unit of speed is metres per minute (metres/minute) which is written in short form as m/min.
(3) The small values of speed are expressed in the units of ‘centimetres per second’ which is written in short form as cm/s. The very small speeds are expressed in the unit of millimetres per second (mm/s).
(4) The large speed values are expressed in the units of kilometres per hour which is written in short form as km/h. When the distance travelled is measured in kilometres and the time taken is measured in hours, then the speed will come in the unit of ‘kilometres per hour. The speeds of fast moving objects like cars, trains and aeroplanes are usually expressed in the unit of kilometres per hour.
The very large speed values are expressed in the units of kilometres per second (km/s). For example, a space rocket has a very, very large speed, therefore, the speed of a space rocket is normally expressed in the units of kilometres per second (km/s).
Speedometer and Odometer
An instrument on a vehicle’s dashboard which indicates the speed of the vehicle when it is running, is called speedometer. The speedometer has the symbol km/h written on its dial.
Odometer is an instrument for measuring the distance travelled by a vehicle. Odometer records the distance travelled by a vehicle in kilometres. We can usually see a small rectangular window within the speedometer dial with the symbol ‘km’ written on its right side. This gives us the odometer reading for the distance covered by the vehicle.
The meter fitted on the top of the handles of scooters and motorcycles is the speedometer. It shows the speed of the running scooter or motorcycle. This meter has also an inbuilt odometer for recording the distance covered
Some animals move slowly and have low speeds whereas other animals can run (or fly) very fast and they can have high speeds.
Uniform and Non-Uniform Motion
When the speed of an object moving along a straight line path remains the same (or unchanged), we say that the speed is constant. If the speed of an object moving along a straight line path keeps changing (increasing or decreasing), we say that the speed is not constant. So, depending on the nature of its speed, a moving object may have uniform motion or non-uniform motion.
An object moving along a straight line path is said to have uniform motion if its speed remains constant. An object having uniform motion travels equal distances in equal intervals of time.
A car running at a constant speed is an example of uniform motion. A car running at constant speed will cover equal distances in equal intervals of time.
In the case of uniform motion, the average speed of the moving object is the same as its actual speed.
An object moving along a straight line path is said to have non-uniform motion if its speed keeps changing. An object having non-uniform motion travels unequal distance in equal intervals of time.
The non-uniform motion (in which the speed of an object keeps changing) is also called accelerated motion.
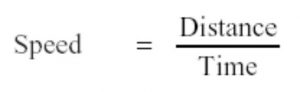
Hello maam thanks for all this content . i am studying cbse class 7 syllabus
Very good explanations….Very helpful to us for studying the important points.
Its good sharing ma’am. Thanks.
Thanks for sharing this information, it is really helpful for understanding all the concepts.
it is nice website i wish it was a app
thanks mam to share your knowledge with us it is very use full
Very nice explanation, very helpful for exams.